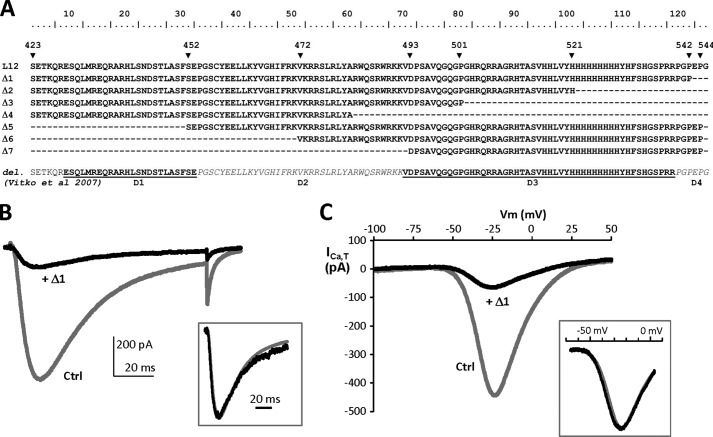
FIGURE 2.
Design of short (Δ) I-II loop constructs and representative electrophysiological properties of the Δ1 construct. A, the amino acid sequences of the Δ1–Δ7 constructs were identified according to the human Cav3.2 protein entry in the UniProt database (O95180): Δ1 (Ser423–Pro542), Δ2 (Ser423–His521), Δ3 (Ser423–Pro501), Δ4 (Ser423–Ala481), Δ5 (Ser452–Pro544), Δ6 (Val472–Pro544), and Δ7 (Asp493–Pro544). These constructs are compared in this multiple alignment with the Cav3.2 deletion mutants (D1–D4) used in Vitko et al. (15). B, superimposed representative T-type current traces recorded using a test pulse at −30 mV from a holding potential of −100 mV (100-ms duration) on HEK-293 cells transfected with Cav3.2 and Nter constructs (Ctrl; gray trace) and Cav3.2 and Δ1 constructs (+Δ1; black trace). The traces were normalized in amplitude (inset), which revealed no difference in the activation and inactivation kinetics of the residual Cav3.2 current in cells expressing the Δ1 construct. C, representative T-type currents recorded using a ramp test (−100/+100 mV; holding potential, −100 mV; 200-ms duration) on HEK-293 cells transfected with Cav3.2 and Nter constructs (Ctrl; gray trace) and Cav3.2 and Δ1 constructs (+Δ1; black trace). Traces were normalized in amplitude (inset), revealing no shift in the current-voltage relationship of the residual Cav3.2 current in cells expressing the Δ1 construct.