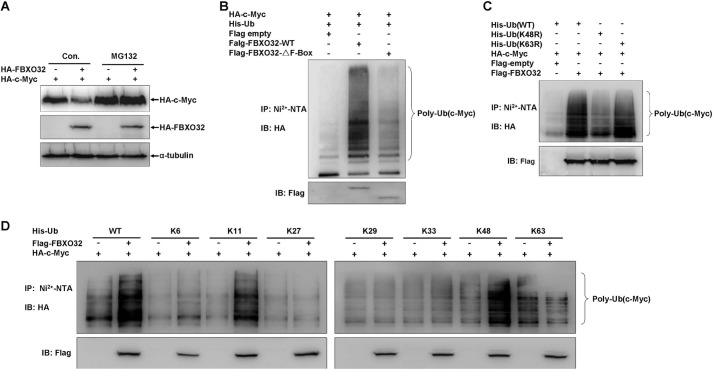
FIGURE 4.
FBXO32 catalyzes c-Myc for Lys-48-linked ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. A, the proteasome inhibitor MG132 blocks FBXO32-induced c-Myc degradation. HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-c-Myc together with either HA-FBXO32 or empty vector; MG132 (20 μm) was added to the medium 6 h before protein harvest. B, the wild-type FBXO32 (FLAG-FBXO32-WT) catalyzes c-Myc ubiquitination, but when the F-box is deleted, the mutant (FLAG-FBXO32-ΔF-Box) reduces its catalytic capability dramatically for c-Myc ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-c-Myc and His-Ub-WT or alone with FLAG-FBXO32-WT or FLAG-FBXO32-ΔF-box; 24 h after transfection, lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation by Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid beads and then were detected by Western blot using anti-HA antibody. C, the wild-type FBXO32 (FLAG-FBXO32-WT) catalyzes c-Myc for Lys-48-linked ubiquitination but not for Lys-63-linked ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-c-Myc and FLAG-FBXO32 or alone with His-tagged wild-type ubiquitin (His-Ub-WT), His-tagged ubiquitin 48 Lys/Arg mutant (Ub-K48R), or His-tagged ubiquitin 63 Lys/Arg mutant (His-Ub-K63R); the ubiquitination assays were performed as in B. D, Lys-48-linked ubiquitination catalyzed by the wild-type FBXO32 (FLAG-FBXO32-WT) was further confirmed by seven Lys-only ubiquitin mutants, Lys-6, -11, -27, -29, -33, -48, and -63. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot.