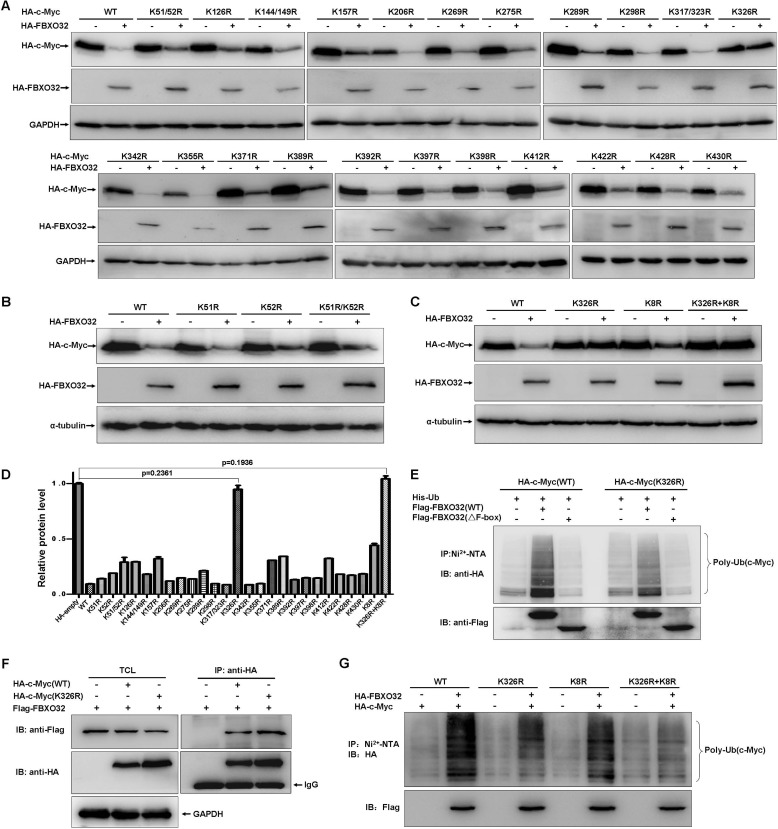
FIGURE 5.
FBXO32 targets c-Myc ubiquitination at K326. A, HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated c-Myc mutants together with either FBXO32 or empty vector. The expressions of c-Myc were detected by Western blot analysis using anti-HA antibody. B, degradation of the c-Myc mutants, K51R, K52R, and K51R/K52R induced by FBXO32 was further confirmed. C, degradation of the c-Myc multiple mutant, K8R, was further confirmed. D, protein levels were quantified based on band density obtained in Western blot assays; the protein level with HA empty vector transfection was treated as 1; the statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism version 5.0 (unpaired Student's t tests); the protein level with HA empty vector transfection was treated as 1. E, the catalytic capability of FBXO32 on c-Myc(Lys-326) polyubiquitination is reduced significantly (the sixth column from the left to the right) compared with that on wild-type c-Myc (the second column from the left to the right). F, the c-Myc Lys/Arg mutant (HA-c-Myc(K326R)), as well as the wild-type c-Myc (HA-c-Myc(WT)), interacts with FBXO32, as revealed by co-immunoprecipitation assays. For ectopic expression, the amount of HA-c-Myc(WT) was 2 times more than that of HA-c-Myc(K326R) (ratio = 1:3) regarding the degradation of wild-type c-Myc by FBXO32. G, the catalytic capability of FBXO32 on the c-Myc multiple mutant (K326R plus K8R) polyubiquitination is further reduced (the eighth column from the left to the right) compared with that on the c-Myc(K326R) (the fourth column from the left to the right). Error bars, S.E. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot.