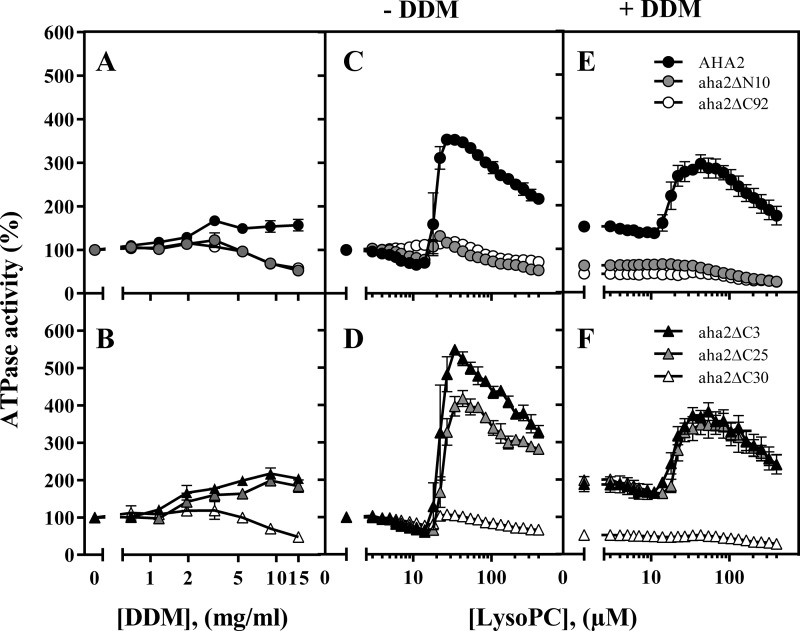
FIGURE 1.
Activation of the PM H+-ATPase by DDM and lyso-PC 16:0 depends on the presence of intact terminal domains. The ATPase activities of membranes isolated from cells expressing either WT AHA2 (●); a variant with an N-terminal truncation (aha2ΔN10; gray circles); a variant with a C-terminal truncation encompassing the entire regulatory domain (aha2Δ92; ○); or variants with three, 25, or 30 amino acids removed from the C terminus (aha2Δ3/25/30; ▴, gray triangles, and ▵, respectively) were analyzed with increasing concentrations of DDM (A and B) or lyso-PC (C, D, E, and F) ±1.5% DDM. Concentrations of DDM refer to concentrations in the preincubation mixture with a membrane protein concentration of 5 mg/ml. The mixture was diluted to 0.4 mg/ml protein and mixed 1:1 with 1 mg/ml dioleoylphosphatidylcholine before assaying the ATPase activity at 30 °C with 3 mm ATP. LysoPC refers to the concentration directly in the assay. An activity of 100% corresponds to the specific activity at 3 mm ATP without lyso-PC (see Table 2 for quantification) (n = 3–5 biological replicates; ±S.E. (error bars)).