Extended Data Figure 1.
Related to Figure 1
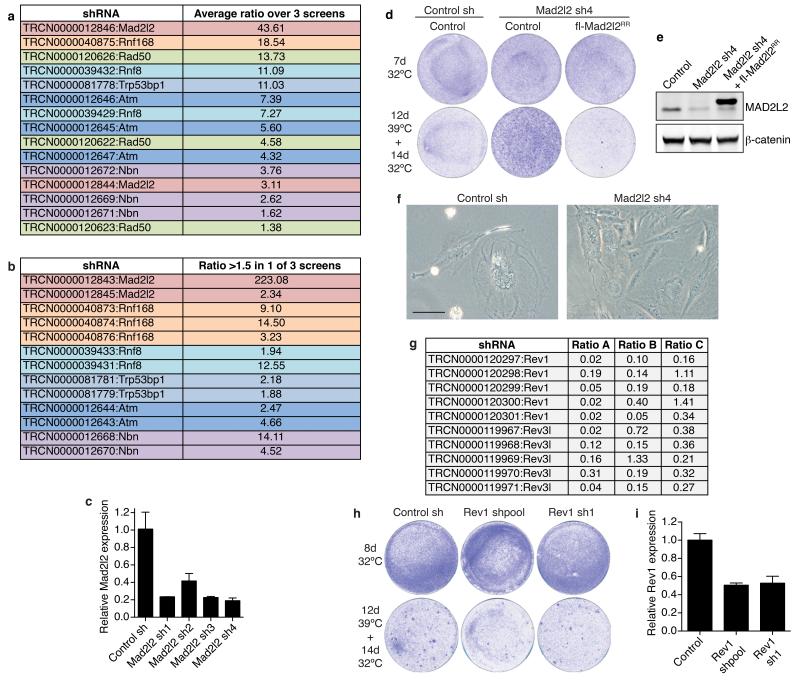
a, A functional genetic screen for telomere-induced genomic instability regulators (TIGIRs) identifies independent shRNAs against Mad2l2 and the previously identified regulators of NHEJ-mediated telomere fusion Atm, Nbs1 (a.k.a. Nbn), Rad50, 53bp1 (a.k.a. Trp53bp1) and Rnf8. Listed are the independent shRNAs enriched >1.5 fold in at least 2 out of 3 TIGIR-screens, with their average ratio of enrichment over all 3 screens. Ratios reflect shRNA abundance after 12 days of telomere uncapping at 39°C followed by 4 days recovery at 32°C versus shRNA abundance after growth for 4 days at 32°C. b, Additional shRNAs targeting Mad2l2 or known TIGIRs that were enriched >1.5 fold in 1 of 3 screens, with their ratio. Not shown are additional shRNAs against factors not previously implicated in control of telomere fusion, that were significantly enriched in these TIGIR-screens but await validation. c, qRT-PCR analysis of Mad2l2 expression levels in TRF2ts MEFs transduced with 4 independent shRNAs targeting Mad2l2 and used in Fig. 1b (Error bars: s.d.). d, Survival assay of TRF2ts cells infected with control or Mad2l2 sh4 shRNAs, complemented with empty control or RNAi-resistant Flag-Mad2l2RR and grown as indicated. e, Western blot showing expression of endogenous MAD2L2 and exogenous Flag-MAD2L2 in TRF2ts cells used in d and in Fig. 1c. f, Photograph of shRNA-transduced TRF2ts cells grown for 12 days at 39°C. Scale bar, 100 μm. g, None of 10 shRNAs targeting Rev1 or Rev3 were significantly enriched in any of 3 independent DDR TIGIR-screens. h, shRNA-mediated Rev1 knockdown does not increase survival upon prolonged telomere uncapping in survival assays of TRF2ts MEFs. Of note, Rev3 knockdown compromised viability and was therefore not informative in these assays. i, qRT-PCR analysis of mouse Rev1 expression levels of cells shown in h (Error bars: s.d.).