Fig. 2.
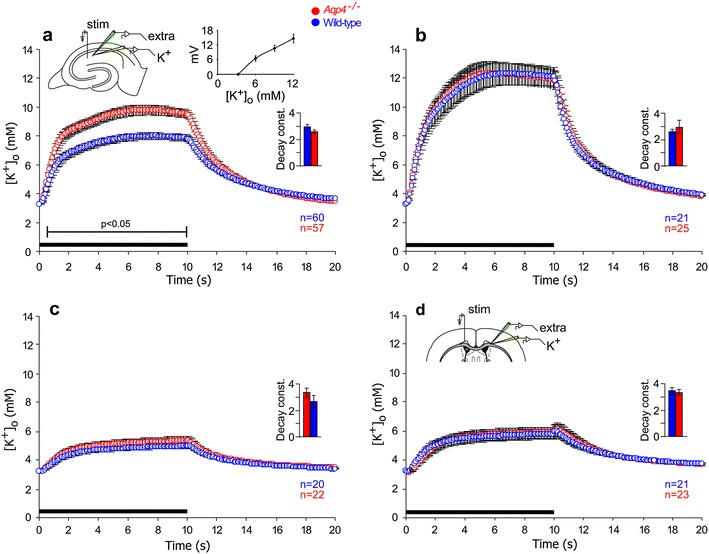
Impact of Aqp4 deletion on extracellular K+ dynamics during synaptic stimulation. a Potassium responses during and after 10 s stimulation at 20 Hz (black horizontal bar along the abscissa) from hippocampal synaptic stratum radiatum layer CA1 of wild type (blue circles, n = 60) and Aqp4 −/− mice (red circles, n = 57). Vertical bars indicate SEM. Bracket indicates period of statistical significant difference (p < 0.05) between genotypes. Insets a schematic drawing of the hippocampal formation with recording and stimulating electrodes; electrode calibration graph for the K+-sensitive electrodes showing the relationship between voltage and [K+]o (bars indicate SD); histogram of the K+-decay constants, measured during the post-stimulation phase (bars indicate SEM). b As in a, but the recordings are from the stratum pyramidale (n = 21 for wild type mice, n = 25 for Aqp4 −/− mice). c As in a, but during blockade of ionotropic glutamate receptors (50 μM AP5 and 20 μM DNQX) thus isolating the changes in [K+]o mediated by axonal activity. The figure shows that [K+]o during and after high-frequency stimulation was similar in the two genotypes (n = 20 for wild type mice, n = 22 for Aqp4 −/− mice). d As in a, but experiments were performed on myelinated fibers of the corpus callosum. Inset a schematic drawing of the corpus callosum with recording and stimulating electrodes (n = 21 for wild type mice, n = 23 for Aqp4 −/− mice)
