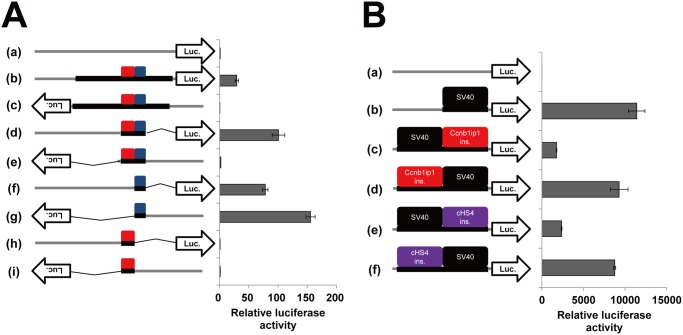
Fig 2. Luciferase reporter assays to evaluate the enhancer-blocking activity of the Ccnb1ip1 insulator.
(A) Identification of the Ccnb1ip1 insulator and enhancer in the 1.8 kbp fragment. DNA fragments and their orientations cloned immediately upstream of luc2 in the pGL4.23 [luc2/minP] vector (a) were: 1.8kbp fragment in the sense orientation (b) and in the antisense orientation (c), 464-bp (nt.886 to nt.1349) fragment in the sense (d) and the antisense (e) orientations, 185-bp (nt.1128 to nt.1312) fragment in the sense (f) and the antisense (g) orientations, and 242-bp (nt.886 to nt.1127) fragment in the sense (h) and the antisense (i) orientations. Cos7 cells were transfected with these vectors and measured for the luciferase activities. Gray and black lines represent the vector backbone and cloned fragments, respectively. Red and blue boxes represent the 242 bp insulator and the 185 bp enhancer, respectively. Luciferase activities relative to that of the control vector (a) are shown (mean ± sd, n = 3). (B) Enhancer-blocking activity of the Ccnb1ip1 insulator against the SV40 enhancer. Red, purple, and black boxes represent the Ccnb1ip1 insulator, cHS4 insulator, and SV40 enhancer, respectively. DNA elements cloned upstream of luc2 in the pGL4.23 vector (a) were: SV40 enhancer (b), SV40 enhancer and Ccnb1ip1 insulator in order of enhancer, insulator, and minimal promoter (c) and in order of insulator, enhancer, and minimal promoter (d), SV40 enhancer and cHS4 insulator in order of enhancer, insulator, and minimal promoter (e) and in order of insulator, enhancer, and minimal promoter (f). Luciferase activities relative to that of the control vector (a) are shown (mean ± sd, n = 3).