Fig. 5.
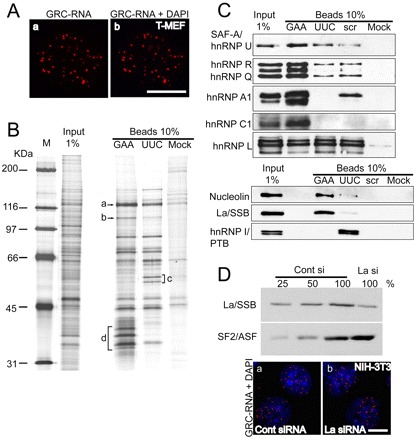
GRC-RNA is associated with the nuclear matrix. (A) GRC-RNA-FISH in nuclear matrix preparations from transformed MEFs revealed the presence of GRC-RNA nuclear foci (a,b). The chromatin was stained with DAPI (blue). The absence of DAPI staining in b is due to DNase I treatment, which degrades most of the nuclear DNA. (B) Isolation of the GRC-RNA binding protein complex. RNA affinity chromatography was performed as described in the Materials and Methods, using affinity matrices containing different RNA sequences [(GAA)15, (UUC)15 and scrambled (scr) RNA oligonucleotides]. For identification, specific bands that showed enrichment were excised, digested with trypsin and subjected to mass spectrometry. a-d represent some of the bands that were excised and analyzed by mass spectrometry (a: hnRNP U; b: nucleolin; c: hnRNP I; d: hnRNP A1, A2/B1, hnRNP C1). (C) Western blot analysis of GAA- and UUC-RNA affinity-purified samples using antibodies against proteins that were identified by mass spectrometry. (D) Depletion of La/SSB in NIH-3T3 cells does not influence the nuclear distribution of GRC-RNA. Immunoblot analysis using La-antibody in cell extracts revealed >75% depletion of La protein in La-siRNA-treated cell extracts. GRC-RNA FISH (red) in control (a) and La/SSB-siRNA-treated (b) NIH-3T3 cells showed similar distributions of GRC-RNA. The chromatin is stained with DAPI. Scale bars: 10 μm.
