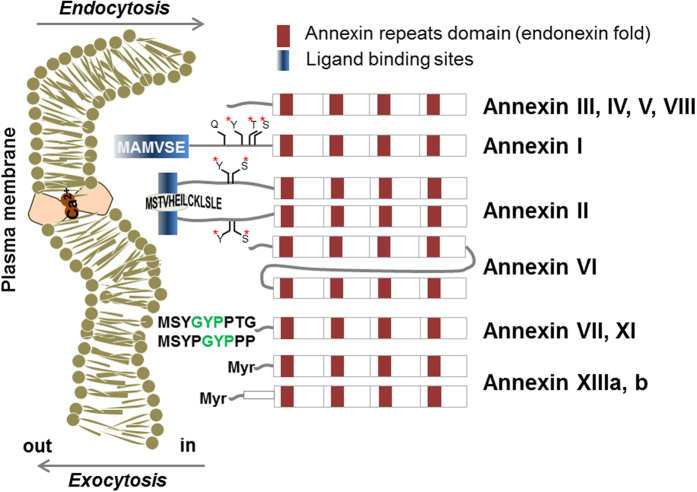
Figure 1. Schematic presentation of annexin isoforms and their N-terminus interacting with plasma membrane Annexin proteins has 12 types in a human form.
Structures of annexins are consists of 4–8 annexin repeats domain that has the endonexin fold (red blocks). Annexin III, IV, V, and VIII has a simple structure having 12–19 residues length of N-terminal domains while annexin XI has a longer length. Annexin I and II have amphipathic α-helices in N-terminus, with phosphorylation sites for serine, threonine, and tyrosine. A glutamine residue is a linking site of a transglutaminase at position 18 in annexin I. Annexin VII and XI has the long N-terminal domain which is composed with glycine, tyrosine, and proline residues (green letters). Annexin XIII is different from other annexins as it has a myristoylation (Myr) of N-terminal domain. All annexins can be transported in and out of plasma membrane via endocytosis or exocytosis with/without calcium ion. This figure describes the endogenous annexins, which has the interaction with extracellular membrane, as proven from the experiment using artificial membrane, such as multivesicular bodies (MVBs)49.