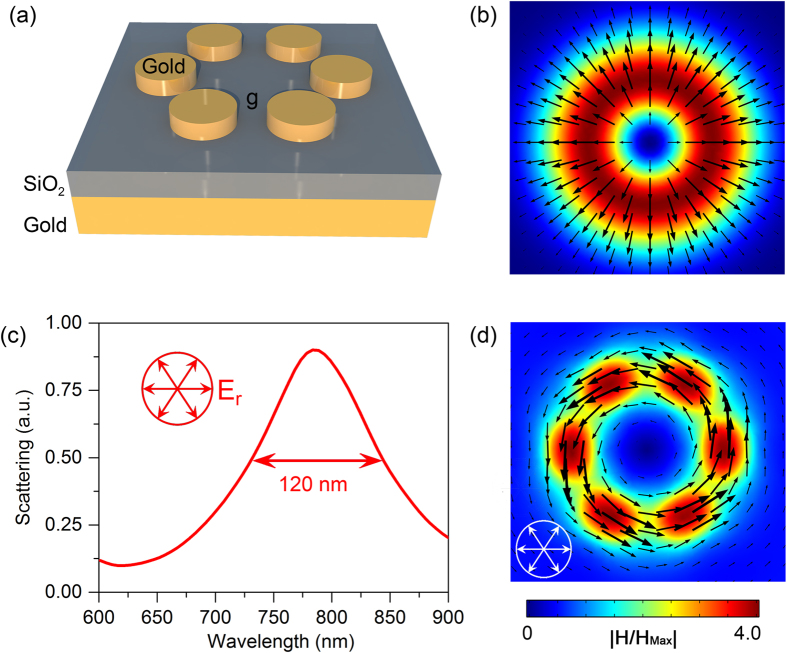
Figure 1. Structure of the toroidal structure and its optical response under radially polarized light.
(a) A schematic view of the toroidal structure composed of a gold hexamer and metallic mirror separated by a dielectric layer. The diameter and thickness of the gold disks are 120 nm and 30 nm, respectively. The thickness of the SiO2 spacer is 30 nm and the thickness of the gold mirror is 60 nm. The gap size between two neighbor gold disks is g = 50 nm. (b) The intensity and field profiles of radially polarized light. The black arrows indicate the vectors of the incident electric fields. (c) The FDTD calculated scattering spectra of the toroidal structure under radially polarized light. (d) The simulated magnetic field at the center of the dielectric layer at the resonance peak of 785 nm. The black arrows represent the vectors of the magnetic fields.