Fig. 3.
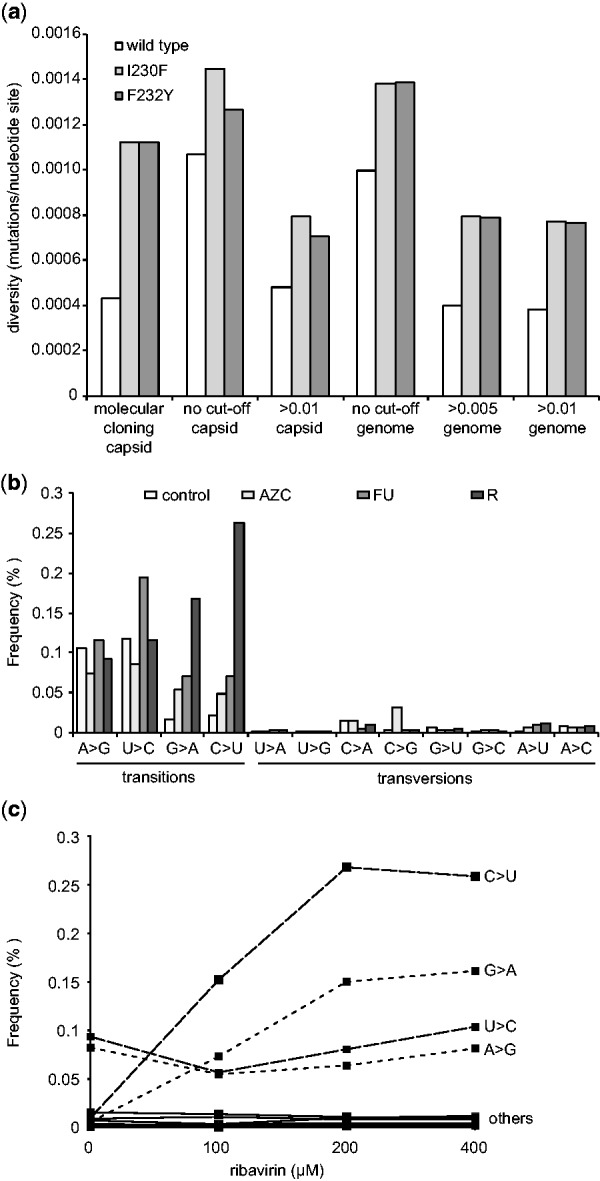
Monitoring population diversity and mutational profiles. (a) The diversity (mutations/nucleotide site) of wild type CBV3 and low fidelity variants I230F and F232Y as previously determined by molecular clone sequencing of a capsid coding region (Gnädig et al), were determined by deep sequencing across the same region (capsid) or across thewhole genome (genome), setting a minimal rate threshold (>0.005 or >0.01) or without a threshold (no cut-off) (b) Transition and transversion biases resulting from mutagen drug treatment. HeLa cells were infected with CVB3 and treated with the mutagens, 5-AZC, 5-FU or ribavirin (R) or left untreated (control). The frequency (% of total virus population) presenting specific transitions and transversions in deep sequence data were classified by ViVan. (c) Dose-dependent effects of mutagen treatment detected by deep sequencing. HeLa cells were infected with CVB3 with increasing concentrations of ribavirin (0, 100, 200 and 400 µM) and the dose dependent increase in the frequency (% of total virus population) of specific transition (C > U, G > A, U > C, A > G; dashed lines) and transversion (labeled ‘others’; solid lines) were determined by ViVan
