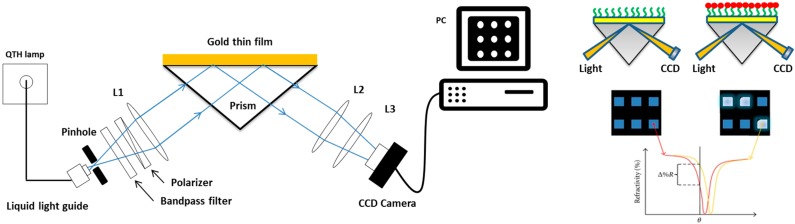
Figure 2.
General principle of surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRI). (Left) The instrumentation of an SPR imaging system: The light source is a quartz tungsten-halogen lamp; the light is delivered through a liquid light guide to a goniometer arm, collimated by lenses, and passed through a narrow interference filter and a polarizer. A p-polarized and monochromatic light beam is then focused directly onto a prism coupler. The reflected light from the gold surface is captured by a monochromatic CCD camera. L2, L3 are lenses positioned in front of CCD for higher quality images. The images could be digitally stored using a B/W frame grabber and further analyzed using photography software; (Right) The analyte-ligand interaction shifts the SPR curve towards a higher angle (red to orange). Due to the measurement confinements (fixed wavelength and angle of incidence θ), changes in the reflectivity (Δ%R) at a single spot of the array can be simultaneously detected. Adapted from [32].