|
| |
| Algorithm 1. Normalized DTW distance. | |
|
| |
Let x, y ∈
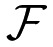 be two finite sequences of lengths N = |x| and M = |y| , respectively. The normalized DTW distance Δ(x, y) is computed as follows: be two finite sequences of lengths N = |x| and M = |y| , respectively. The normalized DTW distance Δ(x, y) is computed as follows: | |
| 1. | Initialize δ(0,0) = 0, δ(n,0) = ∞ for n = 1,…, N and δ(0,m) = ∞ for m = 1,…, M and compute the terms of the DTW matrix, using the difference equation: |
| δ(n, m) = min {δ(n−1,m), δ(n,m−1), δ(n−1,m−1)} + d(xn, xm) | |
| for (n, m) ∈ {1,…, N} × {1,…, M}. | |
| 2. | Initialize ℓ = 0, vℓ = (N, M) and compute the sequence v ∈ ℕ2 as follows: |
| while [vℓ ≠ (1,1)], repeat: | |
| ℓ = ℓ + 1, | |
| vℓ ∈ argmin{δv : v ∈ {vℓ−1 − (1,0), vℓ−1 − (0,1), vℓ−1 − (1,1)}} | |
| end while loop | |
| then K = |v| and w* = {wℓ : wℓ = sK−ℓ +1(v)}. | |
| 3. | The normalized DTW distance between the sequences x and y is Δ(x, y) = k−1δ(N,M). |
|
| |

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.