Figure 1.
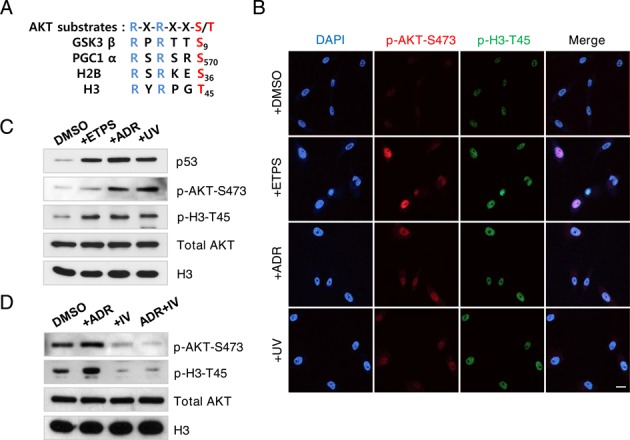
AKT phosphorylates H3–45 in response to DNA damage. (A) AKT substrate sequences conserved in various proteins, including histones H2B and H3. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of phosphorylated AKT-serine 473 (p-AKT-S473) and phosphorylated H3-threonine 45 (p-H3-T45) in MCF10A cells. Cells were treated with DMSO, 100 μM etoposide (ETPS), 0.4 μg/ml adriamycin (ADR) or 50 J/m2 UV irradiation (UV) for 18 h. DNA counterstained with DAPI; scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Western blot of samples in (B). (D) MCF10A cells were treated with DMSO, 0.4 μg/ml ADR, 0.2 μM AKT inhibitor IV (IV) or 0.4 μg/ml ADR and 0.2 μM AKT inhibitor IV for 18 h. Total cell extracts were probed by western blot. Data shown are the representative of three independent experiments.
