Figure 1.
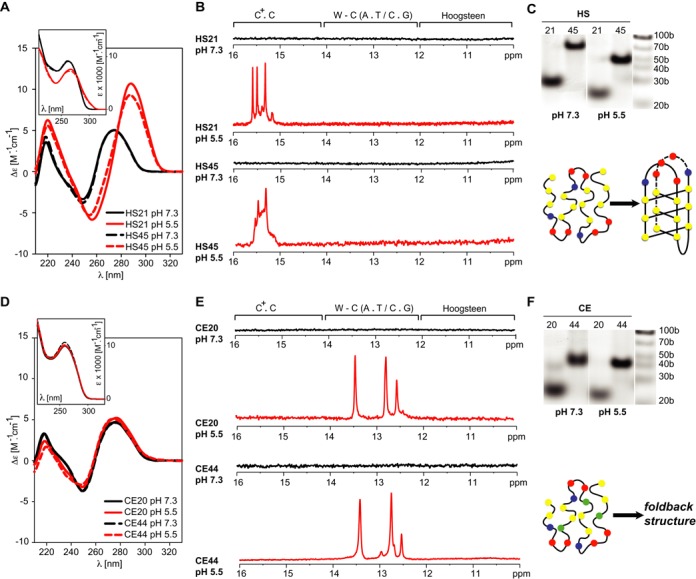
C-rich telomeric DNA from C. elegans and humans forms fundamentally different structures. LEFT: CD spectra of the DNA constructs based on human (A) and C. elegans (D) C-rich telomeric DNA repeats as a function of pH and the number of telomeric repeats. The spectra were acquired at 20°C. The insets show the pH-induced changes in the UV absorption spectra of the constructs. CENTRE: Imino regions of the 1D 1H NMR spectra of the DNA constructs based on human (B) and C. elegans (E) C-rich telomeric DNA repeats as a function of pH and the number of telomeric repeats. The spectra were acquired at 20°C. Regions of the spectra typical of imino protons involved in C.C+, Watson-Crick (W-C) and Hoogsteen base-pairing are indicated. RIGHT: Non-denaturing PAGE of the DNA constructs based on human (C) and C. elegans (F) C-rich telomeric DNA repeats as a function of pH and the number of telomeric repeats.
