Figure 2.
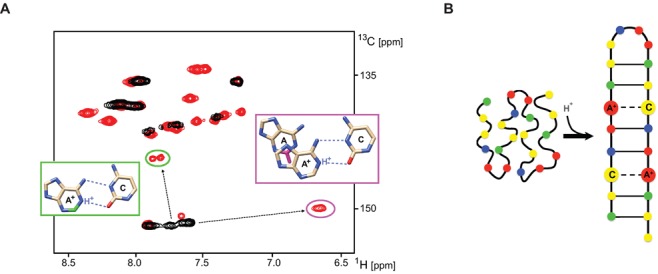
Formation of asymmetrical wobble A+.C base-pair is responsible for pH dependent formation of foldback motif within C. elegans C-rich telomeric DNA. (A) Aromatic regions of the 2D 1H-13C HSQC spectra of the CE21 construct recorded at 10°C and pH = 7.3 (black) and at pH = 5.5 (red). Anomalously shifted cross-peaks (C2/H2) from (two) protonated adenine bases are highlighted in green ellipse. Two anomalously shifted cross-peaks (C2/H2) due to 5′-stacking of non-protonated adenine to the protonated adenine base are highlighted in purple ellipse. Nuclei affected by the adenosine protonation are highlighted in the figure insets: C2-H2 adjoining the protonated N1 of adenosine (green) and C2-H2 exposed to the ring current the from 5′-protonated adenosine (purple). (B) Schematic representation of the low pH-induced foldback motif adopted by C-rich telomeric DNA from C. elegans.
