Figure 2.
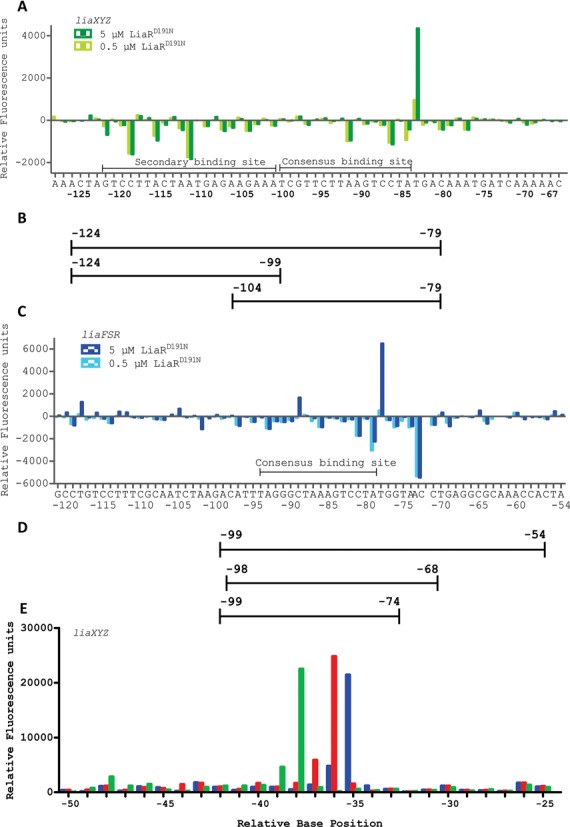
LiaR binds to extended region of DNA that includes sequences outside the proposed canonical consensus sequence. DNase I Footprinting followed by DFACE was used to identify the DNA sequences protected by LiaRD191N within the upstream regions of the liaXYZ (−320 to +30) and liaFSR (−367 to +30) operons of E. faecalis S613. Protection studies were performed at 0.5 and 5 μM LiaRD191N. DNaseI digestion patterns are shown as histograms (A, C, E) where negative changes in relative fluorescence units indicate regions of protection and positives changes indicate hypersensitivity. All DNaseI sensitivity data are relative to a no protein negative control. (A) LiaRD191N binding to the promoter region of the liaXYZ operon. Nucleotide positions refer to the region of LiaR binding (-120 to -77) on the DNA relative to the translation start site of LiaX. (B/D) Oligonucleotides used for DNA binding studies. (C) LiaRD191N binding to the promoter region of the liaFRS operon. Nucleotide positions refer to the region of LiaR binding (−97 to -68) on the DNA relative to the translation start site of LiaF. The AC bar indicates a compression artifact of two bases during electrophoresis seen in both the fragment pattern and the sequencing reaction results. (E) Superimposed electropherograms showing the shift of a hypersensitive location in the upstream region of the liaXYZ operon in response to increasing concentrations of LiaR (blue, 0 μM; red, 0.5 μM; green 5.0 μM). The hypersensitive position shifts from −35(T) to −36(C) to −38(C) in response to increasing protein concentration.
