Figure 5.
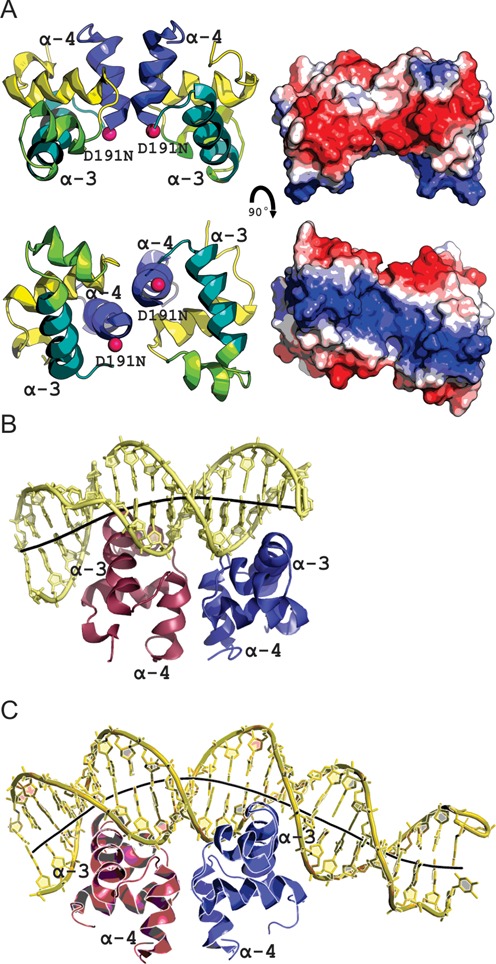
The structure of LiaR(DBD)D191N bound to DNA sequences derived from the liaXYZ consensus and secondary sequences. (A) Structural overview of the isolated DNA binding domain of LiaRD191N. The α4 helices of the LiaR(DBD) (blue) forms part of the molecular recognition surface responsible for formation of the functional dimer required for DNA binding. DNA-recognition helices (α3 from each promoter) are indicated in green. The two α3 helices in the dimer are positioned to create a large electropositive DNA-binding surface. (B, C) LiaR(DBD)D191N bound to DNA sequences derived from the liaXYZ consensus and secondary sites. The LiaR-DNA complex structure shows a strong bend in the DNA, as shown by its helical axis (gray). The helical axis calculated by the program CURVES+ (48) indicated an overall bend of 23.8° and 51.4° for the consensus (B) and secondary (C) sequences, respectively.
