Figure 4.
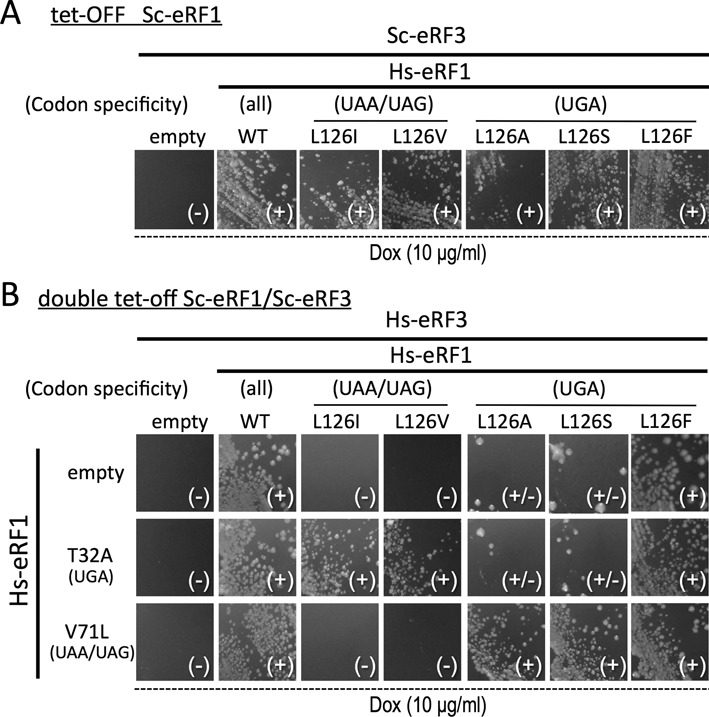
Growth complementation assays for the stop codon specificities of the Hs-eRF1 L126 mutants in the presence of Sc- or Hs-eRF3. (A) Growth complementation assay for single vector transformants of wild type (WT) and L126 mutants of Hs-eRF1 in the presence of heterologous Sc-eRF3 using Sc-eRF1 tet-off strain (S13-D09). Transformants of p416ADH (URA3 marker) (38) harboring each Hs-eRF1 variant grown under permissive conditions were streaked on the SC-Uracil plates containing the stable tetracycline analog (Dox) doxycycline (10 μg/ml) and their colony formation was monitored. (B) Growth complementation assay for dual vector transformants of L126 variants of Hs-eRF1 on p416ADH (URA3 marker) and Hs-eRF1 mutants T32A and V71L (26) on p415GPD (LEU2 marker) in the presence of homogeneous Hs-eRF3 on p414GPD (TRP1 marker) using the Sc-eRF1-Sc-eRF3 double tet-off strain (Y138) (38). Transformants grown under permissive conditions were streaked on the SC-Uracil-Leucine-Tryptophan plates containing the stable tetracycline analog doxycycline (Dox; 10 μg/ml) and their colony formation was monitored. Dox, doxycycline. Codon specificities are indicated: (all) omnipotent, i.e. UAG, UGA, UAA-specific (UAA/UAG) and (UGA) biased to be favorable to ‘UAA and UAG dual-specific’ and ‘UGA-specific’, respectively. Colony growth is indicated as (–) no growth at all, (±) very severe inhibition of growth with several revertant colonies and (+) normal growth.
