Fig. 1.
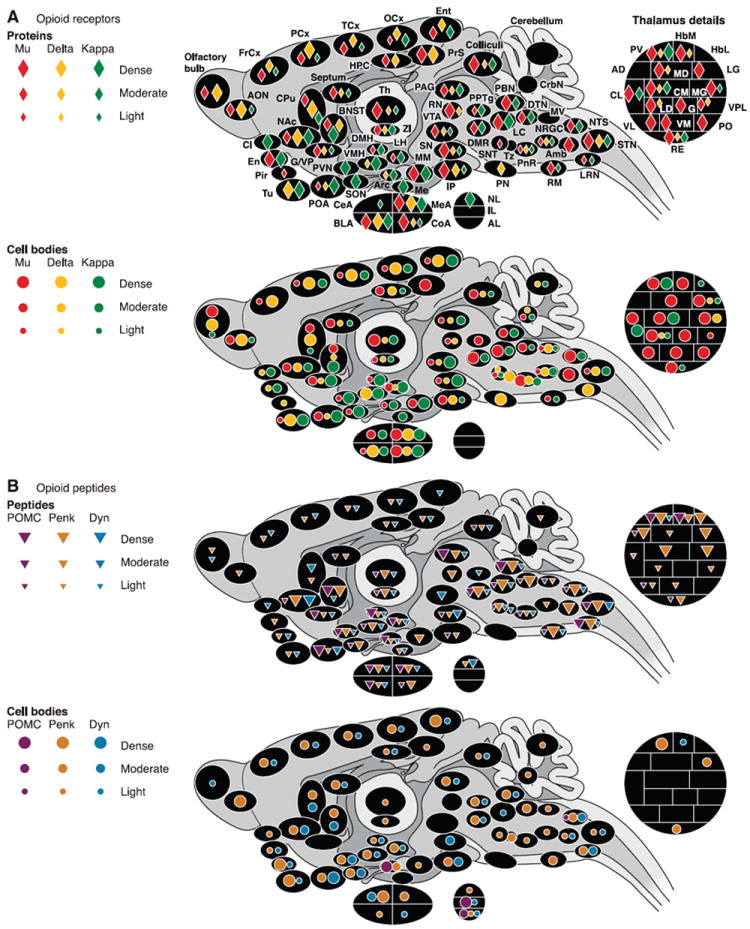
Anatomical distribution of opioid receptors (A) and peptides (B) in the rodent brain (rat and mouse). Only brain regions for which data are available in the literature are represented. Colors correspond to each of the three opioid receptor or peptide precursor. Densities are represented by symbols of different sizes, from low to high. A: receptors. Top panel represents the distribution of opioid receptor proteins as determined by ligand autoradiography. Maximal Bmax (receptor densities, radiolabeled ligands) values reported in the literature for mu and delta receptors were ~170–200 fmol/mg tissue equivalent (IP and olfactory bulbs, respectively). Maximal Bmax values recorded for kappa receptors were 80–100 fmol/mg (Cl; Refs. 144, 193, 346). Bottom panel summarizes the localization of cell bodies expressing opioid receptors based on the detection of mRNAs by in situ hybridization. B: peptides. Top panel depicts the pattern of distribution of opioid peptides by immunohistochemistry. Bottom panel maps cell bodies expressing opioid peptides, as evaluated both by immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization studies. Note: for immunohistochemical mapping, data based on antibodies for peptide precursors were used in priority. When not available, data based on antibodies for final peptides were used, with priority given to peptides issued from a single precursor (β-endorphin and dynorphin). Refer to text for further comments. Amb, nucleus ambiguus; AD, anterodorsal thalamus; AL, anterior lobe, pituitary; AON, anterior olfactory nucleus; Arc, arcuate nucleus, hypothalamus; BLA, basolateral nucleus, amygdala; BNST, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; CeA, central nucleus, amygdala; Cl, claustrum; CL, centrolateral thalamus; CM, centromedial thalamus; CoA, cortical nucleus, amygdala; CPu, caudate putamen; CrbN, cerebellar nuclei; DMH, dorsomedial hypothalamus; DMR, dorsal and medial raphé; DTN, dorsal tegmental nucleus; En, endopiriform cortex; Ent, entorhinal cortex; FrCx, frontal cortex; G, nucleus gelatinosus, thalamus; G/VP, globus pallidus/ventral pallidum; HbL, lateral habenula; HbM, medial habenula; HPC, hippocampus; IL, intermediate lobe, pituitary; IP, interpeduncular nucleus; LC, locus coeruleus; LD, laterodorsal thalamus; LG, lateral geniculate, thalamus; LH, lateral hypothalamus; LRN, lateral reticular nucleus; MD, mediodorsal thalamus; Me, median eminence; MEA, median nucleus, amygdala; MG, medial geniculate; MM, medial mammillary nucleus; MV, medial vestibular nucleus; NAc, nucleus accumbens; NL, neuronal lobe, pituitary; NRGC, nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis; NTS, nucleus tractus solitarius; OCx, occipital cortex; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PCx, parietal cortex; Pir, piriform cortex; PN, pontine nucleus; PnR, pontine reticular; PO, posterior thalamus; POA, preoptic area; PPTg, pedunculopontine nucleus; PrS, presubiculum; PV, paraventricular thalamus; PVN, paraventricular hypothalamus; RE, reuniens thalamus; RN, red nucleus; RM, raphé magnus; SON, supraoptic nucleus; SN, substancia nigra; SNT, sensory trigeminal nucleus; STN, spinal trigeminal nucleus; TCx, temporal cortex; Th, thalamus; Tu, olfactory tubercle; Tz, trapezoid nucleus; VL, ventrolateral thalamus; VM, ventromedial thalamus; VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus; VPL, ventroposterolateral thalamus; VTA, ventral tegmental area; ZI, zona incerta.
