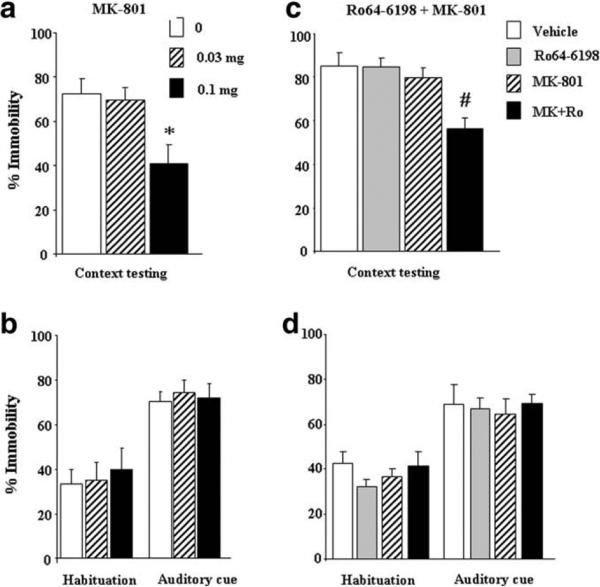
Fig. 2.
Effects of Ro64-6198 and MK-801 on acquisition of contextual and cued fear conditioning. Left panels, (a) and (b): effects of MK-801 (0, 0.03 and 0.1 mg/kg, n = 7–8 per dose) on immobility scores during context and auditory cue testing, respectively. Mice received injections of MK-801 before conditioning and submitted the following day to context and auditory cue testing drug free. Right panels, (c) and (d): effects of Ro64-6198 and MK-801 on immobility scores during context and auditory cue testing, respectively. Mice (n = 7–8 per treatment) received separate or conjoint injections of Ro64-6198 (0.5 mg/kg) and MK-801 (0.05 mg/kg) before conditioning, contextual and cued fear memories were then assessed the following day in separate testing sessions. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM percentage immobility. *p < 0.05, significantly different from vehicle-treated group (Tukey–Kramer post-hoc test). #p < 0.05, significantly different from all other groups (Tukey–Kramer post-hoc test).