Figure 1.
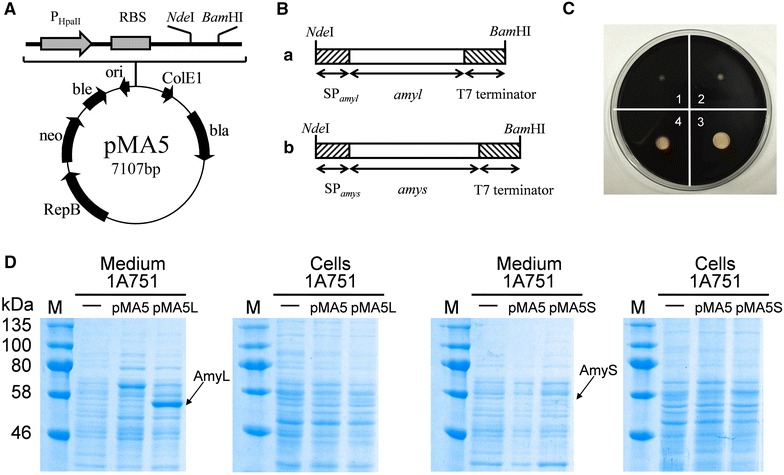
Expression and secretion of α-amylase (AmyL and AmyS) in B. subtilis 1A751. A Vector map of E. coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid pMA5. PHpaII, a widely used promoter from Staphylococcus aureus; RBS, ribosome binding site; ColE1, origin of replication for E. coli; bla, ampicillin resistance; RepB, origin of replication for B. subtilis; neo, kanamycin resistance. B The gene fragments of α-amylase (AmyL and AmyS). Fragment a: AmyL encoding gene containing its native signal peptide SPamyl plus T7 terminator; fragment b: AmyS encoding gene containing its native signal peptide SPamys plus T7 terminator. C Starch hydrolysis of B. subtilis 1A751 (1), 1A751 (pMA5) (2), 1A751 (pMA5L) (3), 1A751 (pMA5S) (4). Strains were grown on LB agar medium containing 1% starch at 37°C overnight. Flood the surface of the plate with 5 mL Gram’s iodine stain. D SDS-PAGE analysis of expression of α-amylase (AmyL and AmyS) in medium and cell fractions by B. subtilis at incubation of 72 h. Lane M molecular weight marker.
