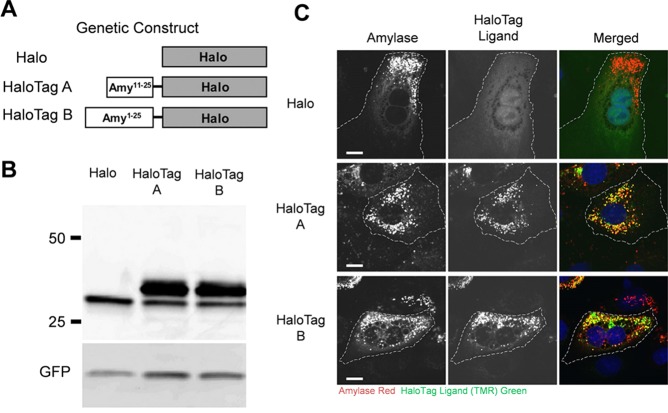
Figure 5.
Intracellular imaging of HaloTag-modified amylase using immunofluorescence microscopy. (A) Two HaloTag–amylase proteins (HaloTag A and HaloTag B) were constructed, as the exact translational start site for salivary amylase has not been identified. (B) Expression of nonconjugated HaloTag (Halo) and both HaloTag A and B proteins was examined. The top band represents the HaloTag complex, whereas the smaller band is indicative of pure HaloTag without amylase attached. (C) Halo, HaloTag A, and HaloTag B were labeled with a HaloTag ligand (TMR-Green), and secretory granules were labeled with an anti-amylase antibody (shown in red). Both HaloTag A and B show colocalization with endogenous amylase, indicating that both were in secretory granules. Scale bar = 10 μm. Reprinted with permission from ref (92). Copyright 2013 the American Physiological Society.