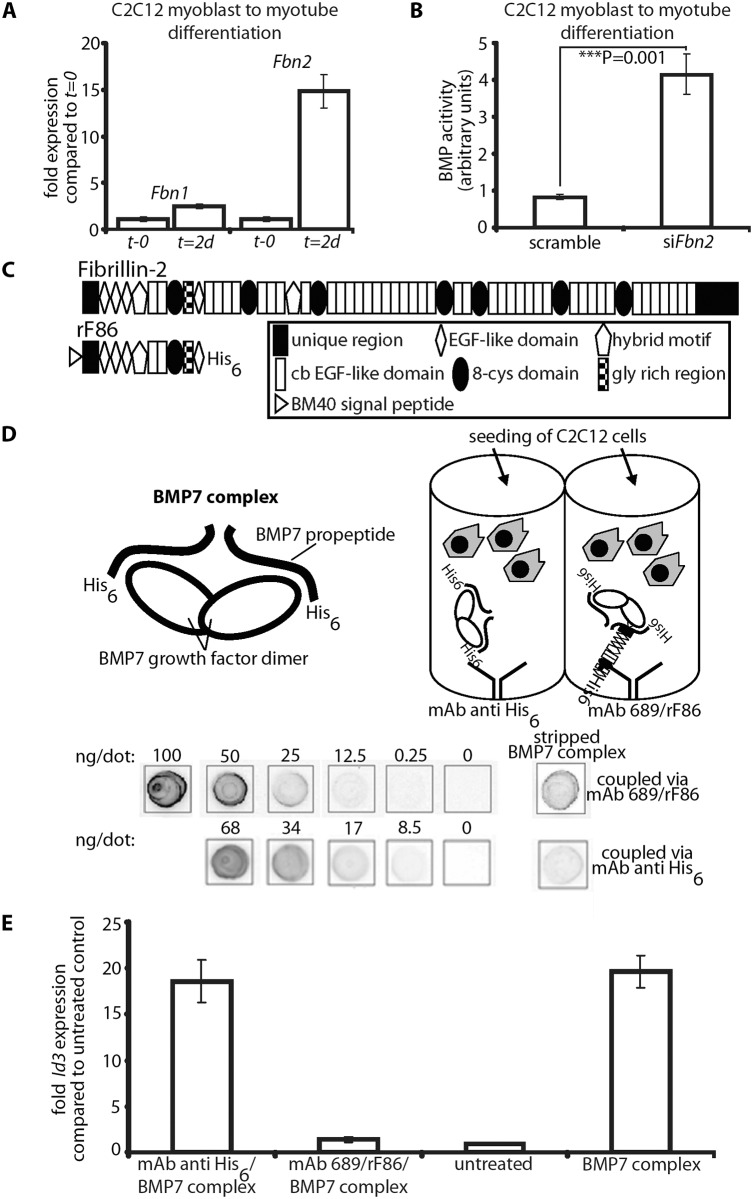
Fig 8. In vitro BMP bioactivity assay using C2C12 cells.
(A) Comparison of Fbn1 and Fbn2 mRNA levels during myoblast to myotube differentiation. (B) BMP activity measured with and without RNAi of Fbn2 during myoblast to myotube differentiation. (C) Domain structure of fibrillin-2 and recombinant polypeptide rF86. (D) Interaction of fibrillin-2 with the prodomain of BMP-7 complex confers latency to the growth factor. Top left: cartoon depicting BMP-7 complex, a growth factor dimer non-covalently associated with two processed prodomains. Top right: cartoon of the assay: BMP-7 complex was coupled via prodomain interactions either through a mAb directed against the N-terminal His6-tag of the BMP-7 prodomain or an N-terminal fibrillin-2 peptide (rF86) which was captured by mAb689. C2C12 cells were then seeded. Below: quantitation of coupled amounts of immobilized BMP-7 complex determined by comparison with standards of known concentration. (E) qPCR expression levels of Id3 from treated and untreated wells. Error bars indicate mean ± SD. Each experiment was performed in triplicates.