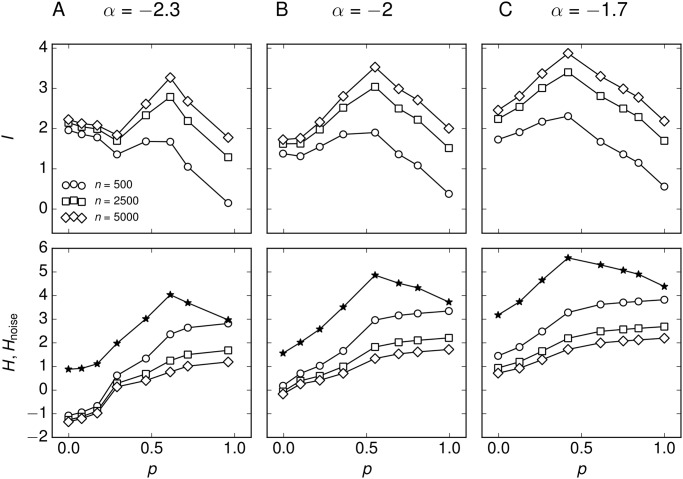
Fig 9. Information transfer of the correlated networks.
(Top row) Mutual information I = H − H noise of the input/output relation of the networks. (Bottom row) Entropy H (stars) and noise entropy H noise (open symbols). (A) The network with large negative exponent α = −2.3 has an optimum in information transfer for slightly higher value of p compared to the other networks. Additionally, its signal transmission capabilities are poorer which is characterized by lower values of I that result from small entropy H due to low firing rates. (B) The network with intermediate exponent α = −2.3 has its signal transmission optimized at an intermediate value of assortativity, p ≃ 0.6. (C) The network with small negative exponent α = −1.7 exhibits the most efficient signal transmission. The mutual information peaks for a relatively low value of assortativity p ≃ 0.4, which means that the uncorrelated network is already quite efficient in signal transmission.