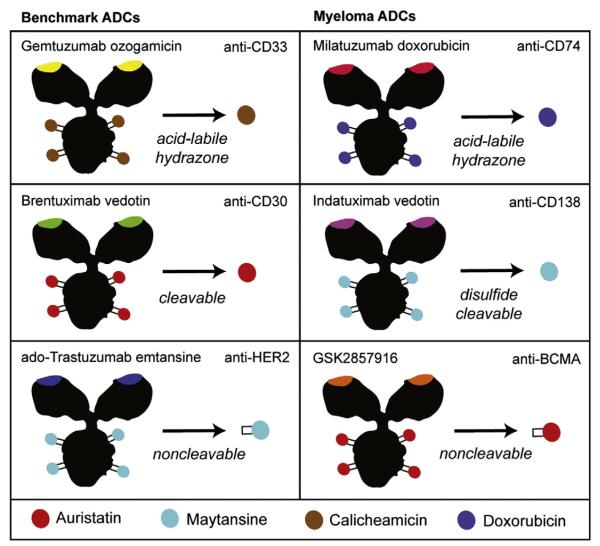
Fig. 2.
Mix-and-match antibody–drug conjugate construction. FDA-approved ADCs (left column) have consisted of gemtuzumab ozogamicin for AML (later withdrawn), brentuximab vedotin for Hodgkin lymphoma and ado-trastuzumab emtansine for breast cancer. The linkers and drugs used for this approach have evolved and diversified over this time. GO used a labile hydrazone linker connected to a DNA-damaging agent, whereas newer ADCs mostly utilize cleavable or non-cleavable linkers with potent antitubulins that optimize intracellular delivery. These technologies, which were pioneered by Seattle Genetics and Immunogen, have been adapted for other malignancies such as myeloma. Examples of ADCs developed for use in myeloma are shown in the right column, showing a mix of constructions similar to the previously FDA-approved agents.