FIG. 8.
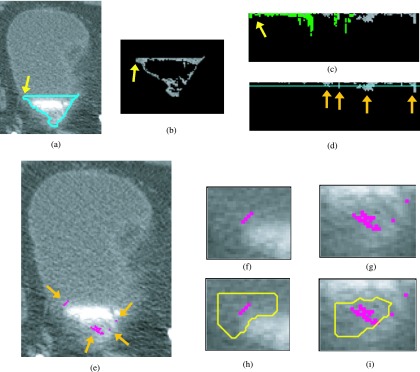
Bladder lesion candidate prescreening and segmentation at a slice near the end of the bladder—example of false positives. (a) Segmentation of the C region of the bladder (L contour). (b) C region image after adaptive thresholding. (c) Bladder wall profile. Highlighted pixels were removed during the false positive reduction of voxel candidate. (d) Bladder wall profile used for candidate detection. The line is the threshold used to determine lesion candidates. The arrows point to lesion candidates. (e) Lesion candidates projected onto the bladder. Arrows point to lesion candidates. [(f) and (g)] Magnified image of the region around the lesion candidate. [(h) and (i)] Lesion candidate segmentation. Two single pixel lesion candidates shown in (e) and (g) were discarded during the lesion candidate determining stage using the size criteria. The two remaining candidates were both false positive lesions and were removed by the LDA classifier.
