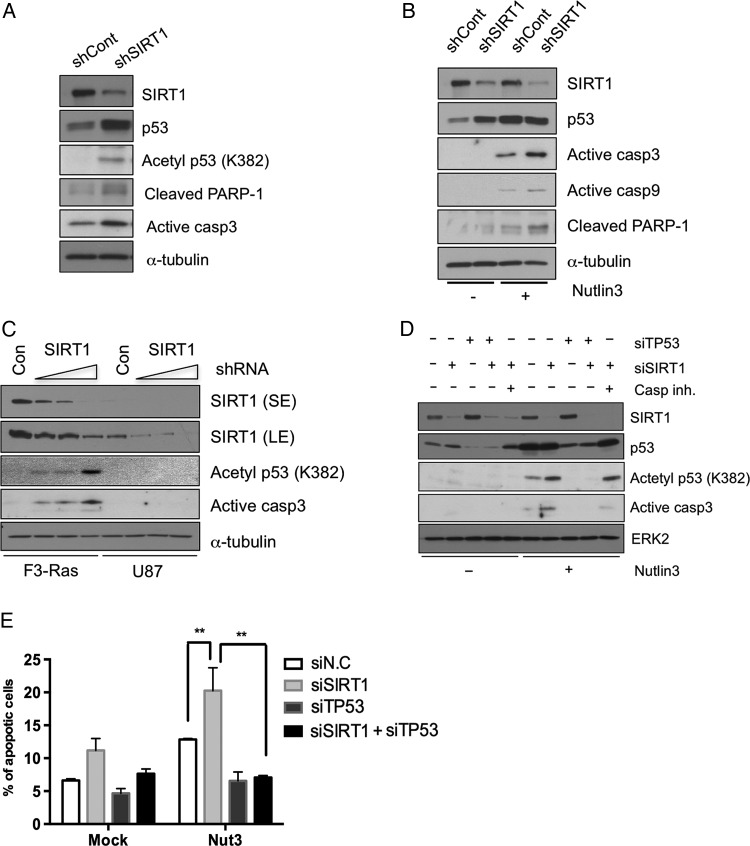
Fig. 5.
P53 is dependent on SIRT1 depletion for cell death in cancer cells with neural stemness. (A) The expressions of SIRT1, p53, acetyl-p53 (K382), cleaved poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1), and active caspase-3 were determined by immunoblotting. (B) F3.Ras.CNSCs (shCont or shSIRT1) treated with Nutlin3 (5 μM) and then harvested after 20 h. The levels of SIRT1, p53, active caspase-3, 9, and cleaved PARP-1 were determined by immunoblotting. (C) F3.Ras.CNSCs and U87 cells underwent a dose-dependent infection. The levels of SIRT1, acetyl-p53 (K382), and active caspase-3 were determined by immunoblotting. (D) F3.Ras.CNSCs were transfected with siRNA negative control (N.C; labeled as ‘-’), SIRT1 (siSIRT1), p53 (siTP53), and SIRT1/p53. The cells were pretreated with a caspase-9 inhibitor when SIRT1 was depleted using siSIRT1, prior to Nutlin3 treatment. The levels of SIRT1, p53, acetyl-p53 (K382), and active caspase-3 were determined by immunoblotting. ERK2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. (E) F3.Ras.CNSCs were transfected with siRNA N.C, SIRT1, p53, and both SIRT1 and p53 and then treated with Nutlin3. These cells were stained with 7-aminoactinomycin and annexin V–phycoerythrin and then analyzed on a conventional flow cytometer. The percentage of apoptotic cell population is presented graphically (n = 4). Alpha-tubulin or ERK2 was loading control.