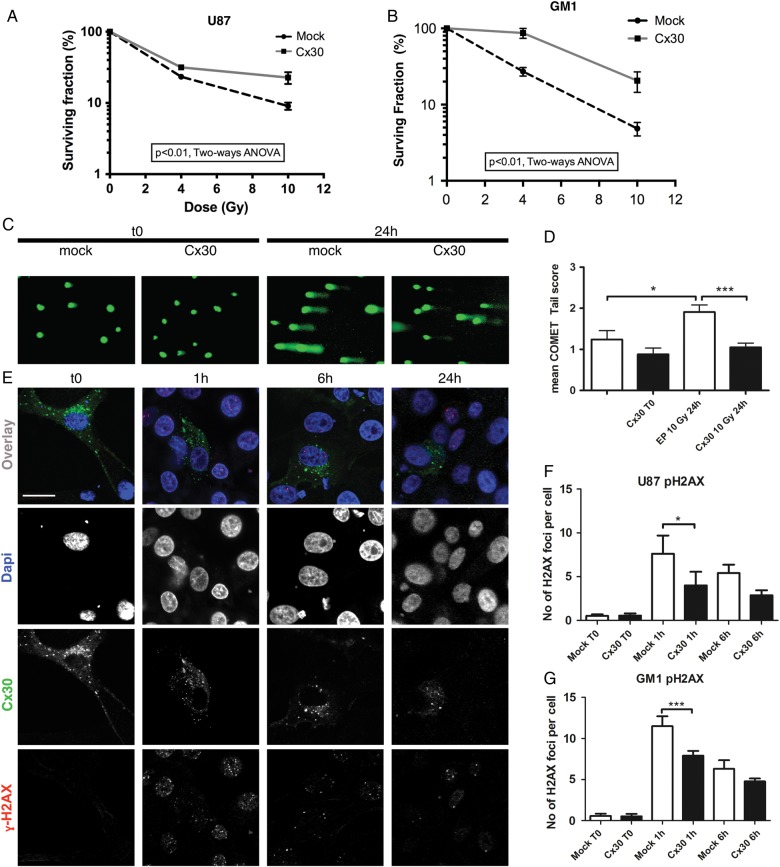
Fig. 3.
Clonogenic assays and DNA damage studies. Clonogenic survival curves assessed at baseline and 10 days after gamma irradiation (4 and 10 Gy) in (A) U87 and (B) GM1 cells expressing Cx30 compared with mock-transfected cells (P < .01 for both cell types, 2-way ANOVA). (C) Illustration of the DNA comet tails observed at baseline and 24 h after gamma irradiation (10 Gy) in Cx30-expressing U87 cells compared with mock-transfected cells. (D) Visual scoring analysis (mean ± SEM, 1-way ANOVA, mock nonirradiated vs mock irradiated cells P < .05, Cx30+ nonirradiated vs Cx30+ irradiated cells P < .001). (E) Confocal immunofluorescence illustration of the gamma H2AX foci at baseline and following gamma radiation treatment in Cx30-expressing cells. Dapi, 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Scale bars = 20 μm. (F) Average number of gamma H2AX foci per cell in U87 cells; at least 100 cells were counted per condition in 3 independent experiments (mean ± SD, 1-way ANOVA, P < .0001, Bonferroni multiple comparison test) and in (G) GM1 cells (at least 150 cells were counted per condition in 3 independent experiments) at baseline and 1 h and 6 h following gamma irradiation (mean ± SD, 1-way ANOVA, P < .0001, Bonferroni multiple comparison test).