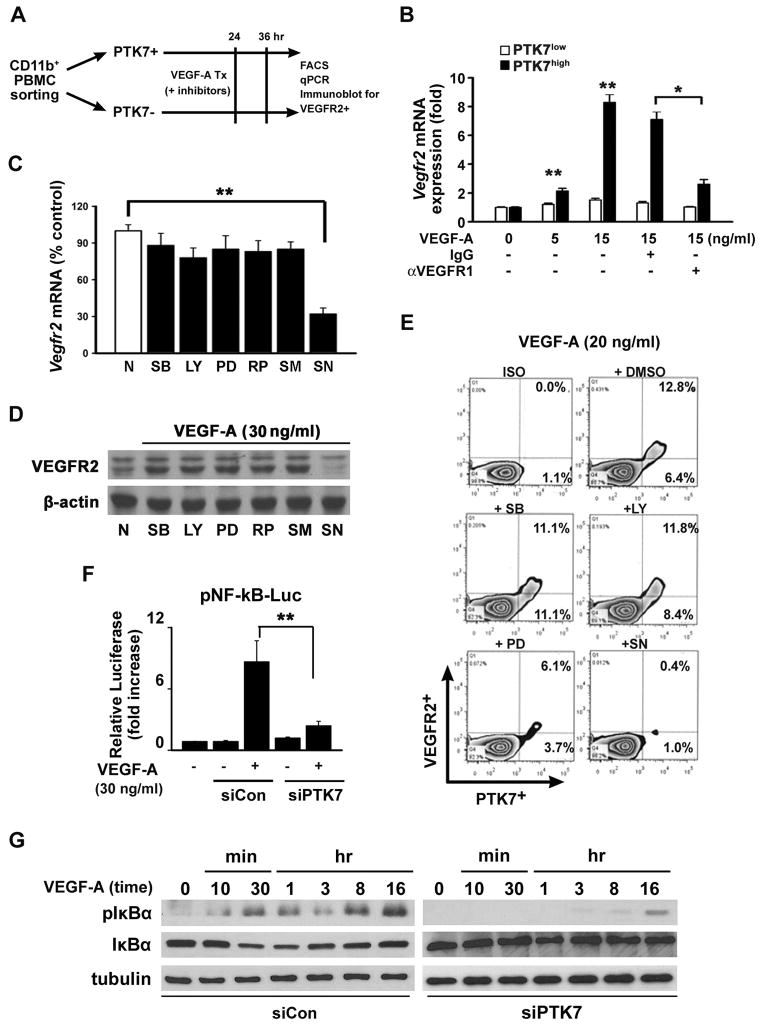
Figure 3. Enhanced VEGFR2 expression in PTK7+ cells is Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB dependent.
A, A schematic illustration showing how PTK7+ and PTK7− cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were separated from VEGF-A pellet-implanted mice using FACS. B, Vegfr2 mRNA expression in PTK7+ and PTK7− cells was measured by real-time qPCR 12 hours after VEGF-A treatment in the absence or presence of 10μM anti-VEGFR1 neutralizing antibody or IgG isotype control antibody. C–E, PTK7+ and PTK7− cells were treated with various signal transduction inhibitors (30 μM; SB: SB203580, LY: LY294002, PD: PD98059, RP: Rapamycin, SM: SN50M, and SN: SN50) 30 minutes before VEGF-A (30 ng/ml) stimulation and then VEGFR2 mRNA (C), protein levels (D), and surface expression levels (E) were determined. F, PTK7 siRNA- or control siRNA-transfected PTK7+CD11b+ cells were cultured with VEGF-A. Two hours after incubation in 10% RPMI, the cells were transfected with NF-κB luciferase constructs for 12 hours. Following 30 minutes of VEGF-A treatment, cells were lysed, and luciferase activities were measured using a luminometer. All data are representative for four independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. **p < 0.01. G, Control siRNA (siCon) or PTK7 siRNA (siPTK7)-transfected cells were treated with VEGF-A (20 ng/ml) as indicated, and western blot was performed using anti-phospho-IκB and anti-IκB antibodies.