Fig. 3.
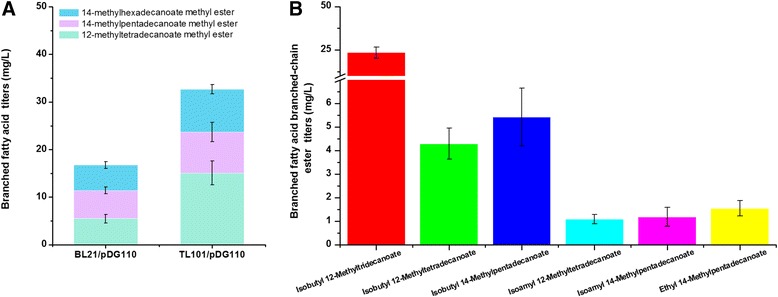
BFA and BFABCE titers in engineered E. coli strains. All experiments were performed in triplicate and SD is indicated. Each color indicated one particular product. a BFA titers in engineered E. coli strains. The total fatty acids were extracted and quantified by GC-MS after esterification with methanol. Pentadecanoic acid was used as the internal standard. 12-Methyltetradecanoate and 14-methylpentadecanoate were confirmed by their corresponding standard methyl esters which were made by esterification of BFA standards and methanol (Additional file 5). 14-Methylhexadecanoate had no available standard and was identified by comparing the mass spectrum to that of corresponding standard in the mass spectral libraries and that of relatively similar branched products. b BFABCE titers in engineered E. coli strains. The BFABCEs were quantified by GC-MS when methyl pentadecanoic acid was used as the internal standard. Except for isobutyl 12-methyltridecanoate, which was identified by comparing the mass spectrum to that of the corresponding standard in the mass spectral libraries, all BFABCEs were identified by the standard made by esterification of the corresponding fatty acid standards and alcohols (Additional file 5)
