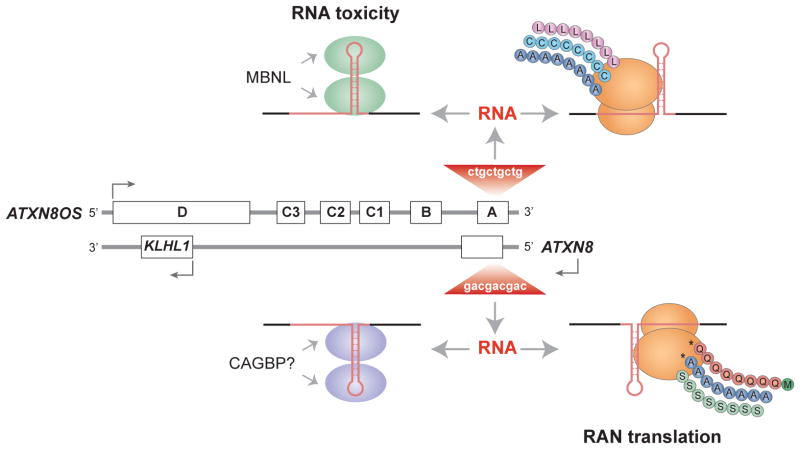
Fig. 4.3.
Bidirectional transcription across microsatellite expansions may generate both pathogenic RNAs and proteins. Transcription of a CTGexp mutation in the ATXN8OS gene (composed of noncoding exons A–D) produces toxic RNA hairpins (red) that either sequester the MBNL proteins or produce polyLeu (L, pink circles), polyCys (C, turquoise) or polyAla (A, blue) by RAN translation. Transcription of the CAGexp on the opposite strand (ATXN8) results in RAN-generated polyGln (Q, orange), polyAla (A, blue) or polySer (S, green) homopolymer polypeptides or a toxic RNA that might sequester an unknown rCAGexp binding protein (CAGBP). While all six RAN proteins are observed in transfected cells, only polyGln (asterisk), which is initiated with a conventional methionine codon (green) in ATXN8, and polyAla (asterisk) have been detected in vivo.