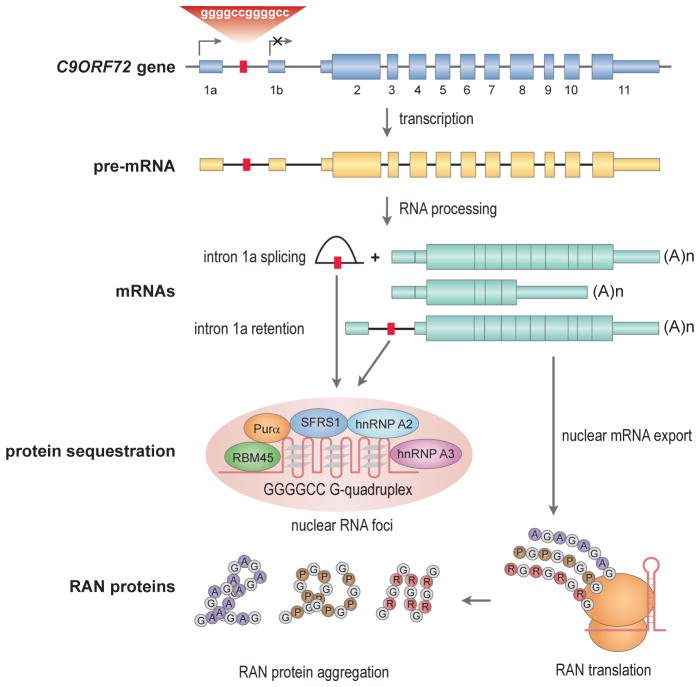
Fig. 4.4.
Toxic RNAs and peptides in C9ORF72 ALS/FTD. The GGGCCexp mutation (red box) in C9ORF72 intron 1a blocks transcription initiation (arrow) from exon 1b but promotes initiation from exon 1a. RNA processing generates at least two mRNAs and a released intron 1a lariat (or intron 1a might be retained during alternative splicing) that may fold into a G-quadruplex and accumulate in nuclear foci (pink ellipsoid) together with multiple nuclear RNA-binding proteins (RBM45, Purα, SFRS1, hnRNP A2, hnRNP A3). Further repeat expansion may lead to failure of this retention mechanism due to titration of rGGGCCexp-binding factors leading to nuclear export of intron 1a-containing mRNA, RAN translation and RAN protein aggregation.