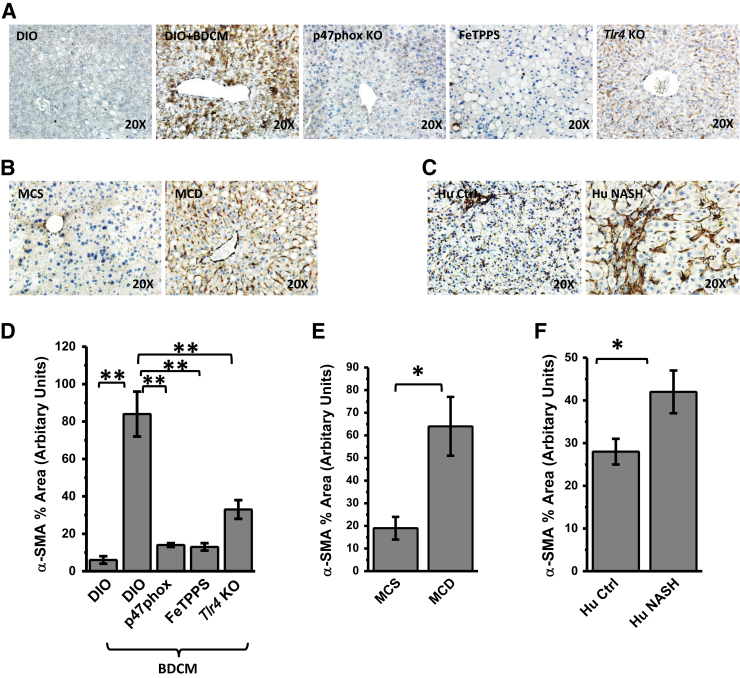
Figure 6.
A–C: Representative images of 5-μm-thick immunostained liver sections, imaged using bright-field microscopy. Positive immunoreactivities (brown) are due to diaminobenzidine binding to respective biotinylated secondary antibodies via streptavidin–horseradish peroxidase. Nuclei (blue) counterstained with Mayer's hematoxylin solution. Immunoreactivities detected are for stellate cell proliferation marker α-smooth muscle actin (SMA). D–F: Morphometries performed on three independent fields for each sample including representative images for percentage of area showing positive immunoreactivity of α-SMA in A (D), B (E), and C (F), calculated in arbitrary units. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. Original magnification, ×20 (A–C). DIO, diet-induced obesity wild-type mouse; DIO + BDCM, DIO mouse exposed to bromodichloromethane (BDCM); FeTPPS, DIO mouse exposed to BDCM and iron(III) tetrakis(p-sulfonatophenyl)porphyrin; Hu Ctrl, healthy human control; Hu NASH, human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; MCD, methionine- and choline-deficient diet–fed mouse; MCS, methionine- and choline-sufficient diet–fed mouse; p47phox KO, high-fat diet–fed mouse with p47phox gene knockout exposed to BDCM; Tlr4 KO, high-fat diet–fed mouse with Tlr4 knockout exposed to BDCM.