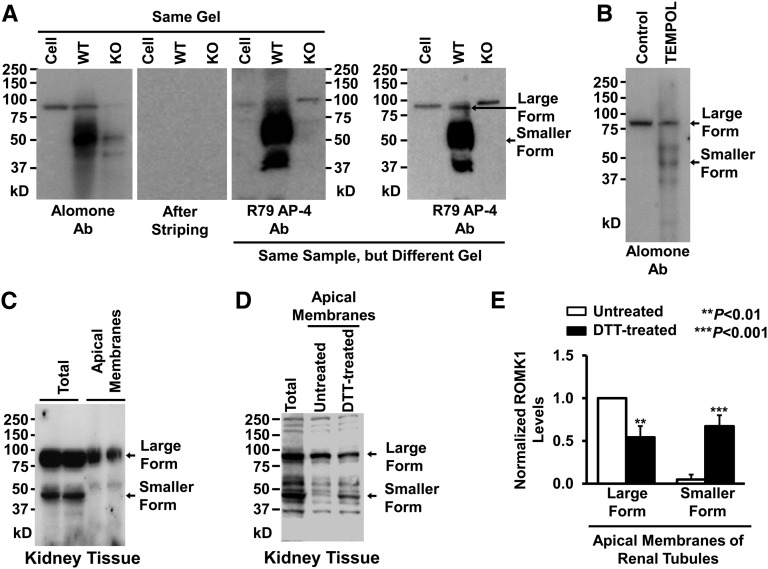
Figure 1.
ROMK1 on Western blots runs at a higher molecular mass than expected in cultured mpkCCDc14 cells. (A) Western blots from mpkCCDc14 cells or kidney tissue of wild-type (WT) or ROMK knockout (KO) mice. (Left panel) ROMK1 channels in the same gel were first probed with a commercial ROMK1 antibody from Alomone Laboratories (Alomone Ab), and then, the membrane was completely stripped and reprobed with another ROMK1 antibody provided by Paul Welling at the University of Maryland Medical School (R79 AP-4 Ab). (Right panel) ROMK1 channels in a different gel were also detected with R79 AP-4 Ab. (B) Western blot from either control mpkCCDc14 cells or the cells treated for 24 hours with 250 μM TEMPOL, a superoxide dismutase mimetic and ROS scavenger. (C) Both the higher molecular mass form of ROMK1 and the lower molecular mass form were detected in lysate from whole kidney, whereas only the higher molecular mass form of ROMK1 was detected in apical membrane protein extract from in situ biotinylated renal tubules. (D) Treatment of apical membrane protein extract of renal tubules with 100 mM DTT decreased the higher molecular mass form and increased the lower molecular mass form of ROMK1. (E) Summary plots of the two forms of ROMK1 in apical membranes of renal tubules in the absence or presence of DTT. Methods for preparing cell lysates are the same for mpkCCDc14 cells and kidney tissue. Each experiment was repeated three times and showed consistent results. DTT, dithiothreitol.