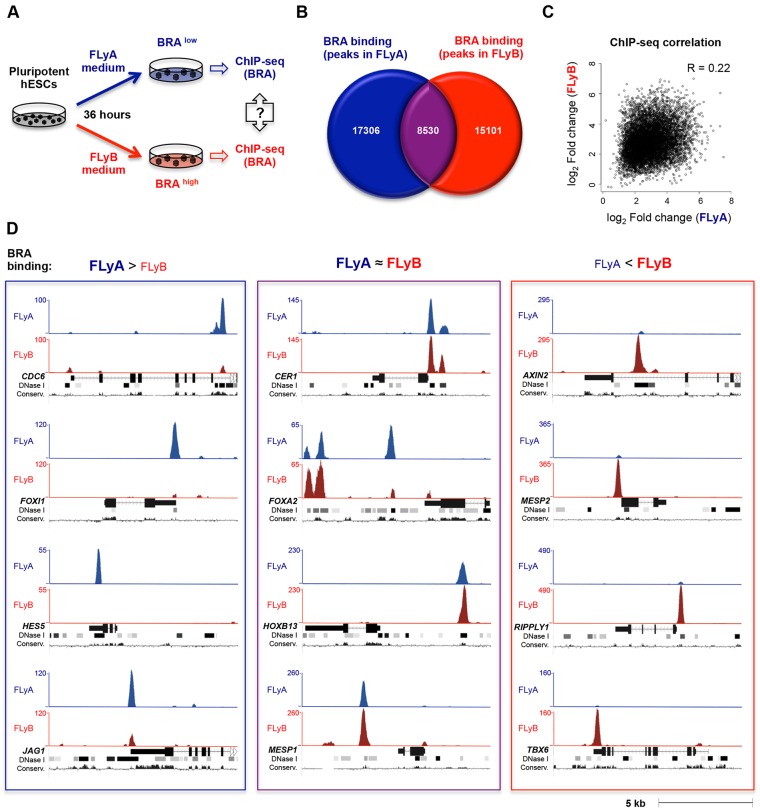
Fig. 2.
BRA exhibits distinct genomic binding profiles in FLyA- and in FLyB-differentiated hESCs. (A) hESCs treated with FLyA (BRAlow) or FLyB (BRAhigh) media for 36 h were used to analyse and compare the genome-wide binding of BRA (ChIP-seq). (B) Venn diagram showing the detectable overlap between BRA binding (ChIP-seq peaks) in FLyA- and FLyB-treated hESCs. (C) Dot plot of ChIP-seq fold enrichment values (normalised to Input samples) of common BRA peaks in FLyA- and FLyB-treated hESCs. R, correlation coefficient. (D) Examples of ChIP-seq peaks depicting BRA-binding profiles in hESCs treated with FLyA (blue track) or FLyB (red track) media: stronger peaks in FLyA (left); peaks detected in both FLyA and FLyB (centre); stronger peaks in FLyB (right). Tracks under ChIP-seq peaks: gene locus (exons depicted as full rectangles, introns depicted as lines with chevrons), DNase I-hypersensitive clusters (ENCODE project) and mammalian conservation profiles (UCSC genome browser). The y axis shows the number of normalised unique reads.