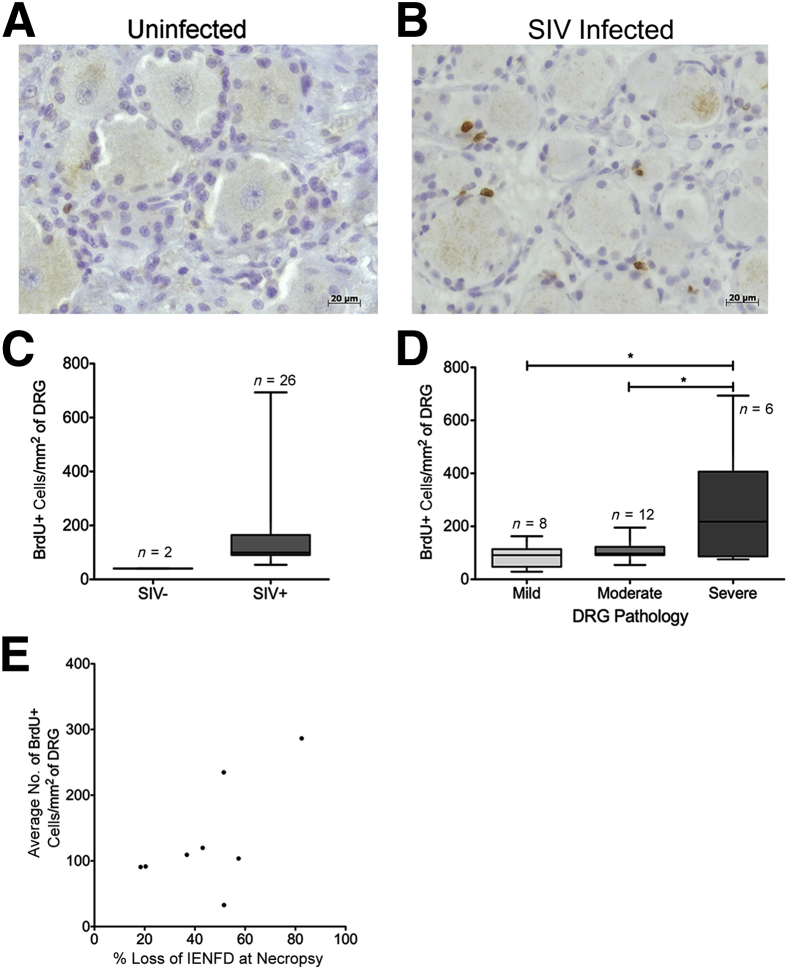
Figure 5.
Cell traffic from the bone marrow to the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) measured by increased 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU+) cells with SIV infection. Animals were serially injected with BrdU to label recently divided monocytes in the bone marrow and then traffic to DRG. A: DRG of uninfected animal A02 with scant BrdU immunoreactivity (brown). B: DRG of SIV-infected animal A06 with marked increase in BrdU immunoreactivity (brown). C: The box plot shows the absolute number of BrdU+ cells per mm2 in SIV− and SIV+ DRGs. The absolute number of BrdU+ cells per mm2 of DRG tissue was calculated. D: The box plot shows the absolute number of BrdU+ cells per mm2 in mild, moderate, and severe DRGs. Higher numbers of BrdU+ cells correlate with the severity of DRG pathology. Analysis of variance (P < 0.01) was performed, followed by post hoc t-tests. E: The average number of BrdU+ cells in the DRGs per animal was calculated. Increased numbers of BrdU+ cells in the DRG correlate with percentage loss of intraepidermal nerve fiber density (IENFD) at necropsy. Spearman correlation was used. Data are given as means ± SEM (C and D). n = 4 (C, SIV− DRGs); n = 26 (C, SIV+ DRGs); n = 8 (D, mild DRGs); n = 12 (D, moderate DRGs); n = 6 (D, severe DRGs). ∗P < 0.05 (r = 0.064).