Fig. 8. Displaced intrauterine device (IUD) with ruptured ectopic pregnancy in a 33-year-old female having acute pelvic pain.
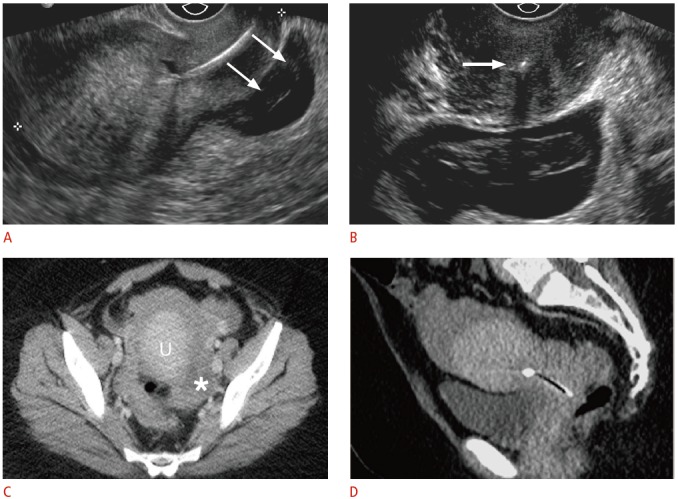
A. Sagittal transvaginal sonogram shows the IUD positioned almost entirely within the cervix with a complex fluid collection posterior to the cervix (arrows). B. Transverse transvaginal sonogram demonstrates internal complexity within the fluid collection, posterior to the IUD positioned within the cervix (arrow). The left ovary was not identified, and computed tomography (CT) was recommended for further evaluation. The pregnancy status was not known at the time. C, D. Axial (C) and (D) sagittal CT show a large amount of hemoperitoneum surrounding the uterus (U) and a complex structure in the left adnexa (asterisk). Human chorionic gonadotropin (β-HCG) level was 595 mIU/mL (normal, <3.0 mIU/mL), and the patient underwent emergent laparoscopy for ruptured tubal ectopic pregnancy.
