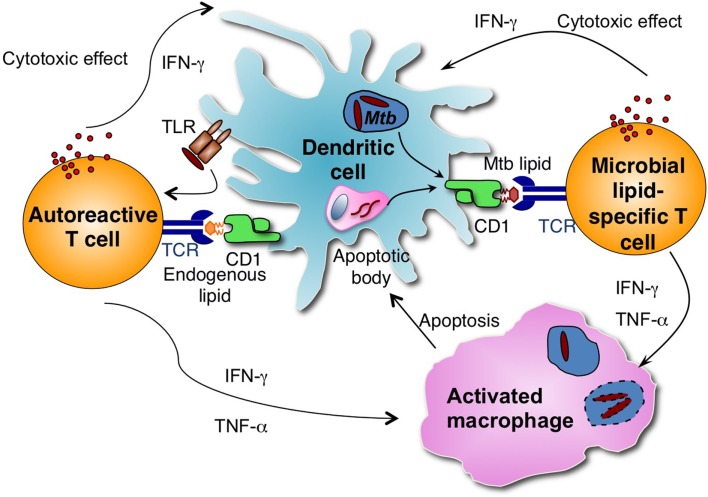
Figure 1.
Group 1 CD1-restricted T cells consist of autoreactive and microbial antigen-specific T cells. Microbial lipid-specific T cells are activated by microbial lipids that are loaded on group 1 CD1 molecules. Autoreactive T cells are activated in combination by proinflammatory cytokines produced on TLR engagement and self-lipid antigens. During Mtb infection, group 1 CD1-expressing DCs can either be directly infected by Mtb or take up apoptotic vesicles from bystander infected cells and present Mtb-derived antigens to group 1 CD1-restricted Mtb lipid-specific T cells. Activated group 1 CD1-restricted T cells are cytotoxic and can directly lyse Mtb-infected cells. Activated group 1 CD1-restricted T cells also produce IFN-γ and TNF-α, which can activate infected macrophages and help to control Mtb growth.