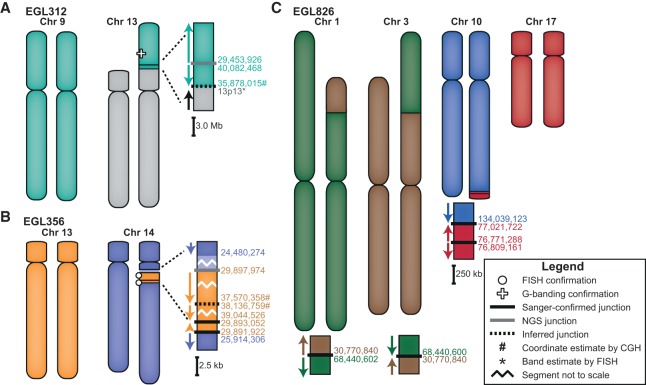
Figure 1.
Models of the complex translocations from EGL312, EGL356, and EGL826. See legend for symbol definitions. Zoomed-in junctions point out those confirmed with PCR and Sanger sequencing, supported only by NGS reads, or inferred by FISH. Lighter-colored chromosome segments are deletions at breakpoints. Arrows indicate chromosomal orientation relative to the normal chromosome and are shown proximal to distal. (A) EGL312 has two regions of Chromosome 9 translocated onto the short arm of Chromosome 13. One NGS breakpoint junction (Nextera mate-pair sequencing) joins the two regions of Chromosome 9, and we infer a second breakpoint junction between Chromosome 9 and Chromosome 13. (B) EGL356's rearrangement is an insertional translocation of three regions of Chromosome 13 into the long arm of Chromosome 14. There is a 1.5-Mb deletion of Chromosome 14 at the insertion site. Nextera mate-pair sequencing revealed translocation junctions between Chromosomes 13 and 14, and we inferred one connection between two Chromosome 13 regions. (C) EGL826 has a maternally inherited balanced translocation between Chromosomes 1 and 3, in addition to a complex unbalanced translocation involving Chromosomes 10 and 17. At this translocation junction, there is an inverted triplication of a region of Chromosome 17. Breakpoint junctions were detected by WGS (Complete Genomics) and confirmed by PCR and Sanger sequencing.