Figure 6. Inhibition of AMPK overcomes acquired resistance to cetuximab via induction of apoptosis.
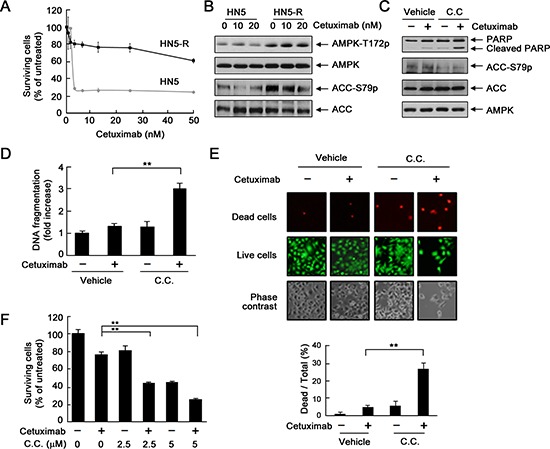
(A) HN5 cells and HN5-R cells were cultured in 0.5% FBS medium containing the indicated concentrations of cetuximab for 5 days and then subjected to MTT assay. (B) HN5 and HN5-R cells were cultured in 0.5% FBS medium in the absence or presence of 10 or 20 nM cetuximab for 24 h. Cell lysates were then prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis with the indicated primary antibodies. (C) HN5-R cells were cultured in 0.5% FBS medium in the presence of 20 nM cetuximab, 10 μM dorsomorphin (C.C. for “compound C”), or both for 24 h. Cell lysates were then prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis with the indicated primary antibodies. (D) HN5-R cells were treated as described in (C). Cell lysates were subjected to a quantitative apoptosis ELISA (Roche Diagnostics). (E) HN5-R cells were treated as described in (C). The cells were subjected to a LIVE/DEAD assay (Life Technologies) and observed under a fluorescent microscope. The ratio of dead cells to total cells in each group was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. **p < 0.01. (F) HN5-R cells were treated with 20 nM cetuximab alone or in combination with 2.5 or 5 μM dorsomorphin for 72 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. The OD values of the treated cells were normalized to the OD value of the untreated cells, which was set as 100%. Data shown are means and SDs (n = 3). **p < 0.01.
