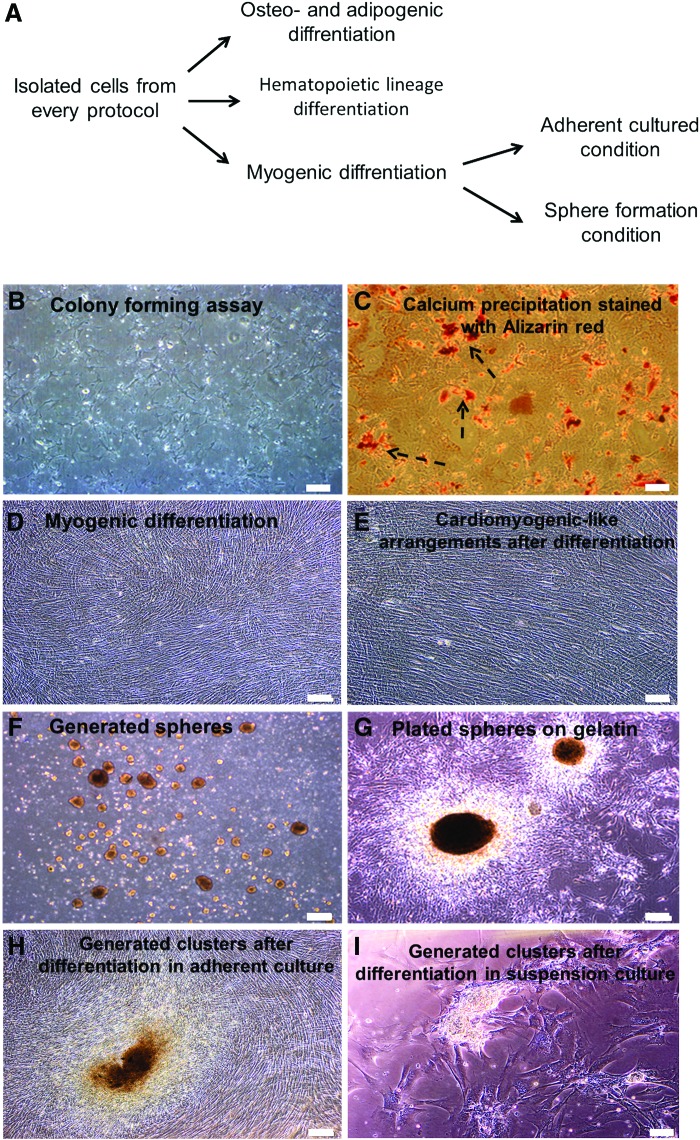
FIG. 3.
Differentiation potential assays. (A) A schematic diagram of our laboratory differentiation protocol. To investigate the differentiation potential of isolated cells we examined their potential for osteogenic, myogenic and hematopoietic differentiation. (B) Fibroblast-like colonies generated in methyl cellulose medium. There were no hematopoietic colonies in methyl cellulose medium that optimized for hematopoietic lineage proliferation. (C) Calcium precipitation in cells stained with Alizarin red after osteogenic differentiation (arrows). (D) Multilayer morphology of differentiated adherently cultured cells. (E) Arrangement of cells in the plate into cardiomyocyte-like cells 2 weeks after the end of differentiation. (F) Sphere formation of CSC on ultra-low attachment plates to evaluate the effect of cell-cell communication on cardiogenic differentiation. (G) Spheres plated on gelatin coated plates at the end of the differentiation procedure. (H) Some clusters generated in plates at the end of the differentiation procedure. (I) Generation of clusters after the end of differentiation procedure in plated spheres. Scale bar=200 μm. As the obtained phenotypic results in all three main cell groups (c-KIT+ cells, CEDCs and CDCs) was the same, figures of only c-KIT+ cells are presented. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd