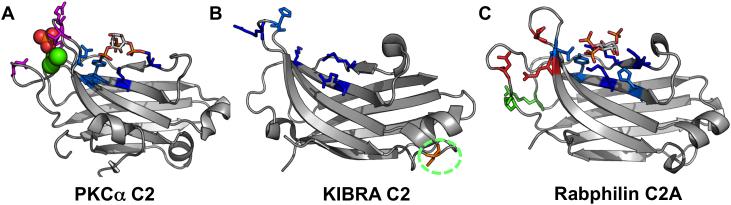
Figure 3. C2 domains have a β-sandwich structure with loop regions adjacent to the “cationic patch”.
These structures have been crystallized with or without inositol headgroups and demonstrate PI-binding through interaction with positively-charged residues in the cationic patch region. PI-binding residues are depicted in blue. Dark blue residues represent positively charged lysines or argininges and light blue are other inositol-headgroup coordinating residues. Residues highlighted in magenta are PS-binding, residues highlighted in green are membrane-inserting, and residues highlighted in red are negative and calcium-coordinating. A. PKCα C2 (3GPE) coordinates PS with Asn189, Arg216, Arg249, and Thr251 where the sulfate is coordinated in the structure (orange and red spheres). In this loop region, negatively charged residues coordinate 3 calcium inos (green spheres) which are crucial to its membrane localization. The PIP2 headgroup is coordinated by Tyr195, Lys197, Lys209, Lys221, Trp245, and Asn253 in the cationic patch region. B. KIBRA C2 (2ZOU) harbors a cationic patch region with Arg753, His755, Arg714, Arg716, Lys692, and Arg696. In addition, Cys771 participates in a disulfide bond between two monomers in the structure. While the molecular basis of WT KIBRA binding to monophosphorylated PIPs such as PI(3)P is unknown, mutation of Met734 or Ser735 alters the C2 domain affinity in such a way it increases the affinity of the C2 domains for PI(4)P, PI(5)P, and PI(4,5)P2 (Duning et al. 2013). C. Rabphilin C2A bound to IP3 (4NP9) coordinates the inositol headgroup in the cationic patch region using Tyr421, Lys423, His425, Lys435, Arg437 and Asn481.