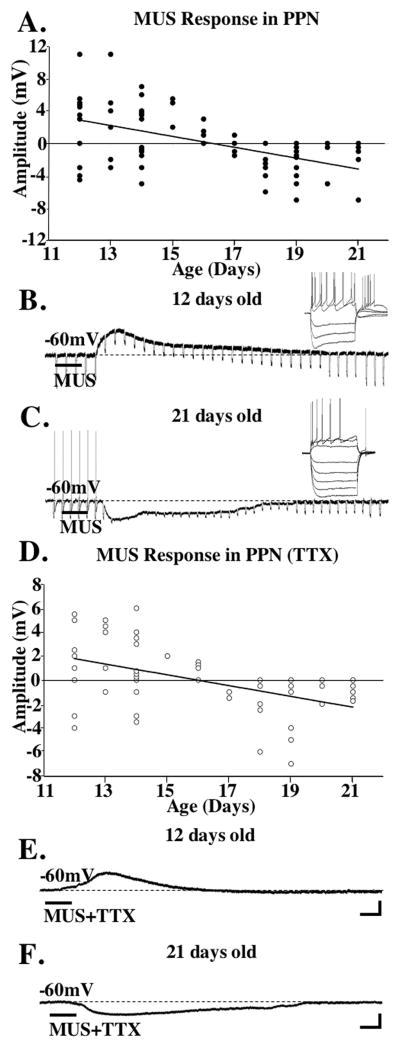
Figure 1. Responses of PPN cells to MUS.
A. Plot of PPN cells recorded after application of MUS across age. Depolarizing responses are above “0”, hyperpolarizing responses are below “0” on the x-axis. Unresponsive cells shown as filled circles on the x-axis with overlapping circles close to “0” denoting no response. The y-axis indicates the maximum membrane change during the response. The regression line is y = −0.6716x + 10.928, R squared = 0.2622. B. Recording from a 12 day type III PPN cell after MUS application. The inset shows depolarizing and hyperpolarizing steps in this LTS cell. C. Recording from a 21 day type II PPN neuron showing a hyperpolarization in response to MUS. The inset shows the presence of Ia conductance in this type II cell. D. Plot of PPN cells recorded after MUS+TTX. The distribution of responses across the two age ranges (12–15 and 17–21 days) was significantly different after MUS (Chi square= 13.02, df=2, p<0.004), and after MUS in TTX (Chi square=7.57, df=2, p<0.02). The amplitude of the depolarization at 12–16 days under MUS before and after TTX was not statistically different (ANOVA df=23, F=0.33, p=0.6). The amplitude of the hyperpolarization at 12–16 days did not differ from that at 17–21 days (ANOVA df=4, F=2.21, p=0.2). The amplitude of the hyperpolarization at 17–21 days under MUS before and after TTX was not statistically different (ANOVA df=13, F=2.21, p=0.16). The regression line is y = −0.4503x + 7.1882, R squared=0.2299. E. Recording from the same cell as in 1B except in TTX. Note the depolarization persisted after sodium channel blockade. F. Recording from the same cell as in 1C showing a hyperpolarization after MUS in TTX. Calibration bars 250 msec and 25 mV for the inset in B, and 2 sec and 3 mV for B and E; 250 msec and 25 mV for the inset in C, and 2 sec and 2 mV for C and F.