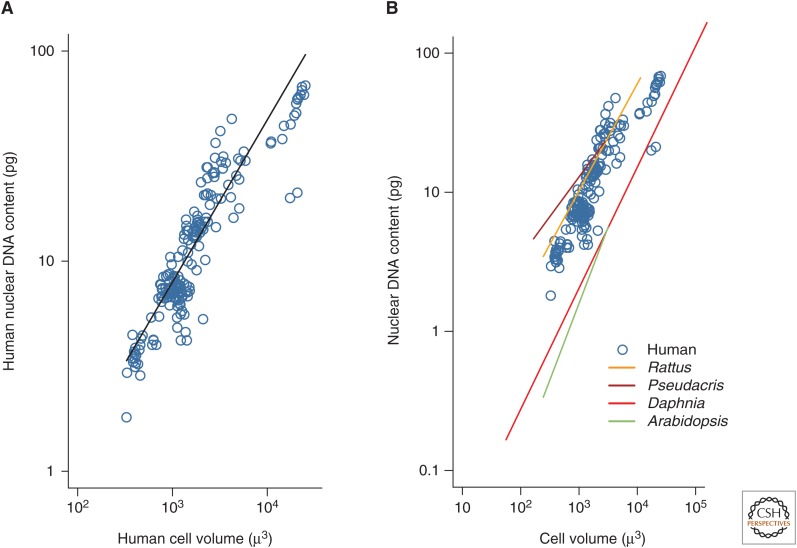
Figure 1.
Mean DNA content for cell populations. (A) Mean nuclear DNA content versus cell volume for healthy human cell populations from 19 cell types (log10 [DNA]) = −1.3 + 0.74 log10 [cell volume], r2 = 0.81; data in Table 1). The characteristic diploid human cell contains 7 pg DNA. (B) Relationship between DNA content and cell size in humans (blue) in comparison to previously reported relationships in the rat (Rattus norvegicus, log10 [DNA] = −1.3 + 0.77 log10 [cell volume] [Heizer 1955]), frog (Pseudacris obscura, log10 [DNA] = −0.6 + 0.57 log10 [cell volume] [Bachmann et al. 1966]), crustacean (Daphnia pulex, log10 [DNA] = −2.3 + 0.87 log10 [cell volume] [Beaton and Hebert 1989]), and plant (Arabidopsis thalania, log10 [DNA] = −3.1 + 1.1 log10 [cell volume] [Jovtchev et al. 2006]). Lines were fitted to data for nonhumans using ordinary least-squares regression. The human data shown here are the same as those shown in A.