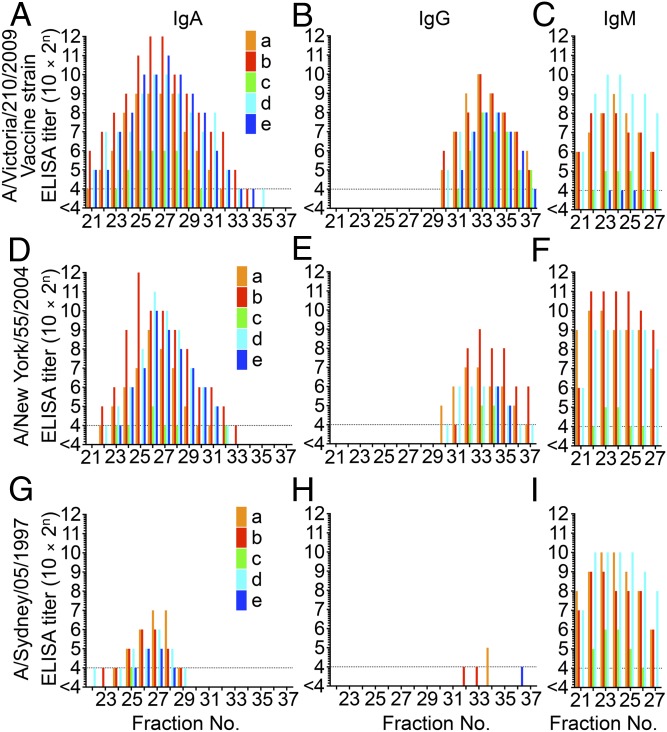
Fig. 2.
Determination of binding activity of antibodies to HA molecules in each GFC fraction by ELISA. The IgA ELISA titer (A), IgG ELISA titer (B), and IgM ELISA titer (C) against HA molecules of Victoria virus (H3N2) were determined in each fraction separated by GFC of nasal wash samples collected from five participants (a, b, c, d, and e aged 33, 23, 27, 24, and 34 years, respectively, at the time of sample collection). HA-specific IgA titers were detected in a broad range of fractions and peaked at fractions 21–30, which corresponded to the first of two peaks of neutralization activity. HA-specific IgG titers peaked at fractions 31–37, which corresponded to the second of two peaks of neutralization activity. The IgA ELISA titer (D), IgG ELISA titer (E), and IgM ELISA titer (F) against HA molecules of NY virus (H3N2) were determined in each fraction separated by GFC of nasal wash samples collected from five participants (a–e). The IgA ELISA titer (G), IgG ELISA titer (H), and IgM ELISA titer (I) against HA molecules of Sydney virus (H3N2) were determined in each fraction separated by GFC of nasal wash samples collected from five participants (a–e). Reduction of the peak titers of HA-specific IgA and IgG antibodies against NY HA (which has 96.6% amino acid similarity to Victoria HA) or Sydney HA (which has 92.9% amino acid similarity to Victoria HA) correlated with decreased sequence similarity to Victoria HA.