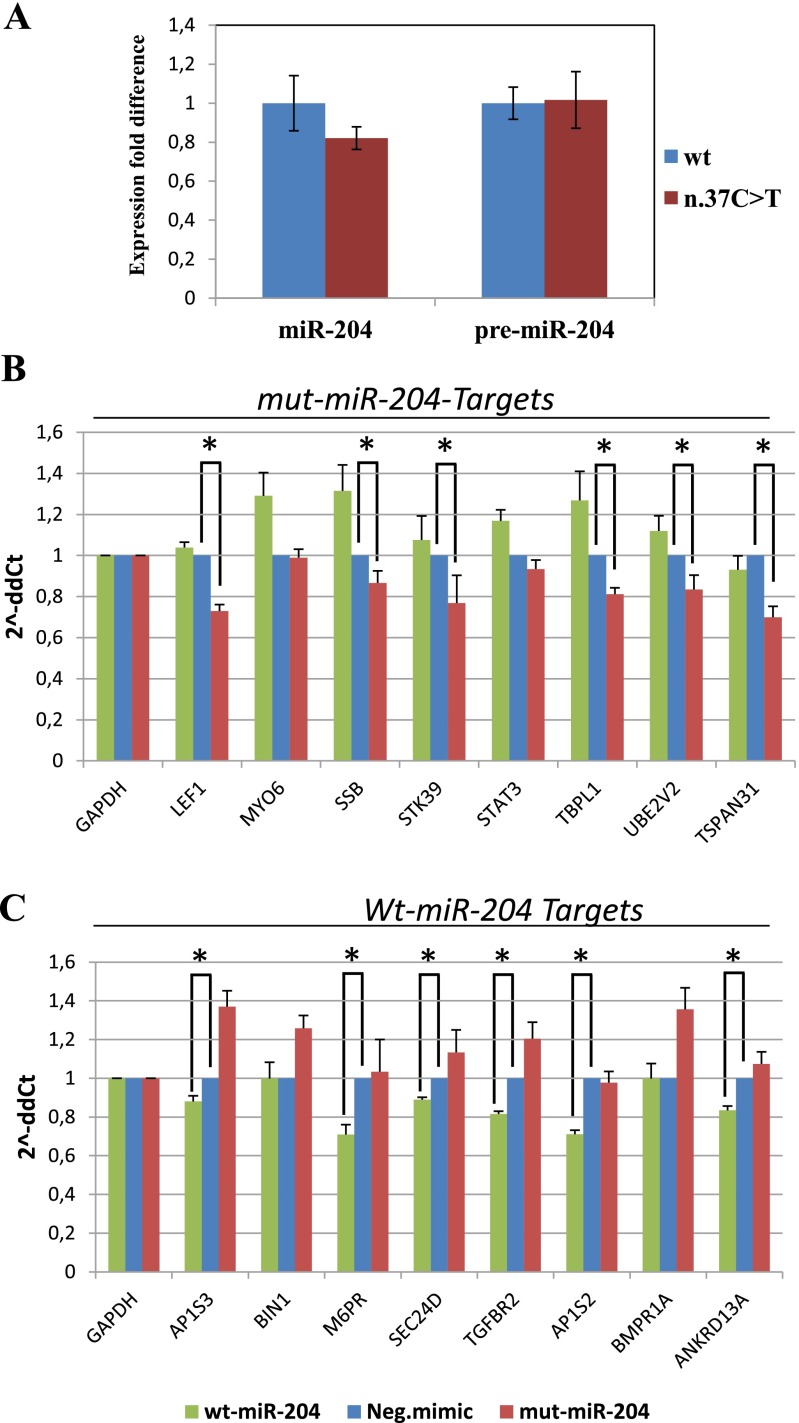
Fig. S2.
Effect of miR-204 mutation on miRNA biogenesis and targeting capabilities. (A) The effect of the n.37C > T mutation on premiR-204 processing was evaluated by qRT-PCR, using a standard curve method. Variations in the expression levels of the mature miRNA and premiR-204 in the mutant (n.37C > T) were compared with the wt levels (set as 1). Values are presented as the mean ± SD (represented as a percentage of variation) of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. Wt-miR-204 mimics (blue bars), mut-miR-204 mimics (red bars). (B and C) qRT-PCR validation of either mut-miR-204–specific (B) and wt-miR-204–specific (C) predicted target mRNAs on total RNA obtained from cells transfected with mut-miR-204 mimics (red bars), wt-miR-204 mimics (green bars), and negative (control) mimics (blue bars). The histograms show expression fold change vs. controls (2^ΔΔCt values, y axis). The GAPDH gene was used to normalize expression levels. Six of eight genes tested in B indeed behave as specific targets for the mut-miR-204, and six of eight genes tested in C behave as specific targets for the wt-miR-204. *Adjusted P < 0.05 in a one-tail t test. ANKRD13A, ankyrin repeat domain 13A; AP1S2, adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma 2 subunit; AP1S3, adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma 3 subunit; BIN1, bridging integrator 1; BMPR1A, bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IA; LEF1, lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1; MYO6, myosin VI; M6PR, mannose-6-phosphate receptor; SEC24D, SEC24 family member D; SSB, Sjögren syndrome antigen B; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STK39, serine threonine kinase 39; TBPL1, TBP-like 1; TGFBR2, transforming growth factor, beta receptor II; TSPAN31, tetraspanin 31; UBE2V2, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 variant 2.