Fig. 6.
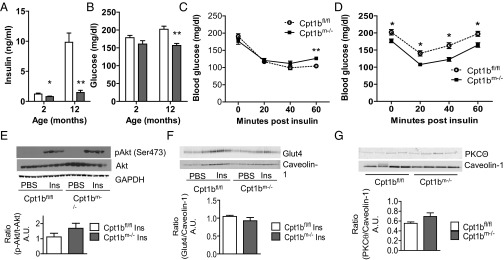
Depletion of Cpt1b in skeletal muscle does not impair whole-body insulin response or muscle insulin signaling. Blood glucose (A) and insulin levels (B) are decreased in Cpt1bm−/− mice after a 4-h fast. There is no difference in response to an ITT in Cpt1bm−/− mice (n = 8–10) at 10–12 wk (C) or 18–20 wk (D). (E) Insulin (Ins)-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt is unchanged in Cpt1bm−/− and Cpt1bfl/fl muscle (n = 4). (F) Similarly, insulin-stimulated translocation of Glut4 to the membrane is unaffected by lack of Cpt1b (n = 3). (G) Membrane-associated levels of PKCΘ are not increased in Cpt1bm−/− mice (n = 4). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 or **P < 0.01, Student’s t test. A.U., arbitrary units.
