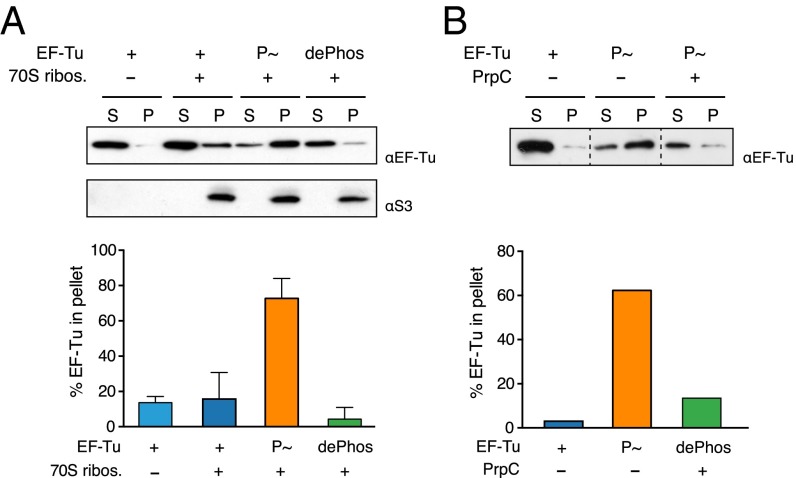
Fig. 4.
EF-Tu–ribosome interaction is stabilized by phosphorylation in vitro. (A) EF-Tu/ribosome cosedimentation assay. Nonphosphorylated (WT), phosphorylated (P∼), or dephosphorylated (dePhos) EF-Tu was incubated with 70S ribosomes in the presence of GTP. A reaction carried out in the absence of ribosomes was used as control. The binding reactions were layered into a sucrose cushion, and the ribosome-bound EF-Tu was separated from the free EF-Tu by ultracentrifugation. The supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were probed with antibodies to EF-Tu and the ribosomal protein S3, and the relative amount of EF-Tu in the fractions was determined by quantitative densitometry and is shown below a representative Western blot. (B) Phosphorylated EF-Tu was incubated with 70S ribosomes in the presence of GTP. The reaction was split, and PrpC phosphatase was added to one half. Both reactions were incubated further for 30 min at 37 °C. Reactions then were pelleted in a sucrose cushion and analyzed as above. Dashed lines separate noncontiguous lanes. Error bars indicate the SD for at least three independent experiments.