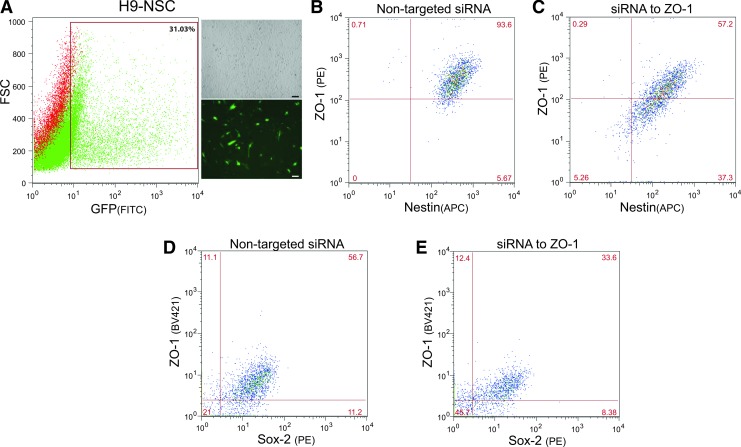
FIG. 7.
siRNA-mediated knockdown of ZO-1 induces less expression of the stem cell marker, Nestin. (A) Indicates the transfection efficiency of H9-NSCs (microscopy images on the right, 10× objective magnification, scalebars at 50 μm) transfected with pooled siRNAs to TJP, ZO-1, together with a siGLO transfection indicator; a FAM-labeled oligonucleotide duplex that localizes to the nucleus. The transfection indicator was used to gate for the transfected cells and a representative graph of the gated population is indicated by the boxed area. (B, D) Representative FACS of immunolabeled ZO-1 and Nestin (B) or ZO-1 and Sox2 (D) on H9-NSCs transfected with control nontargeting siRNA. (C, E) Shows FACS analysis of H9-NSCs transfected with siRNAs to ZO-1 and immunolabeled for ZO-1 and Nestin (C) or ZO-1 and Sox2 (E). Specific knockdown of ZO-1 shows a decrease in the expression of both the TJP and the stem cell markers, Nestin and Sox2. Of note, due to the use of different antibody clones for the BV421 fluorescently tagged ZO-1 and PE fluorescently tagged Sox2, the percent of cells expressing baseline levels of ZO-1 and Sox2 is lower than the more sensitive antibody clones used in Fig. 2.